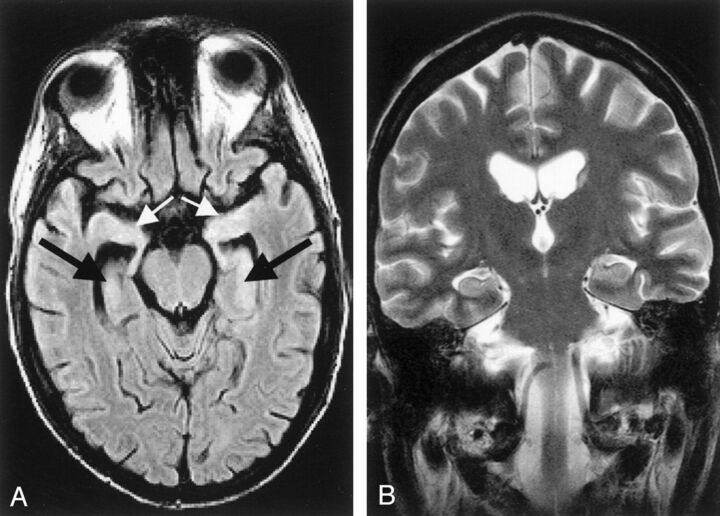
Fig 3.
Acute limbic encephalitis. A 26-year-old man with underlying precursor T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia developed generalized seizures, had short-term memory loss, and was disoriented in time and place 1 month after undergoing unsuccessful allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. At autopsy, multifocal subacute polioencephalomyelitis in the brain regions that were shown as affected on MR images confirmed the diagnosis of paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis with neuronal loss. Initial MR images were obtained 1 day after the first generalized seizure occurred. A, Axial FLAIR image (TR/TE, 9000/110 ms; TI, 2261 ms) shows a slightly elevated signal intensity of both hippocampal formations (black arrows) and amygdala (white arrows). B, Coronal conventional T2-weighted turbo spin-echo image (TR/TE/NEX, 4462 ms/120 ms/3) shows no signal-intensity abnormality.52