Fig 1.
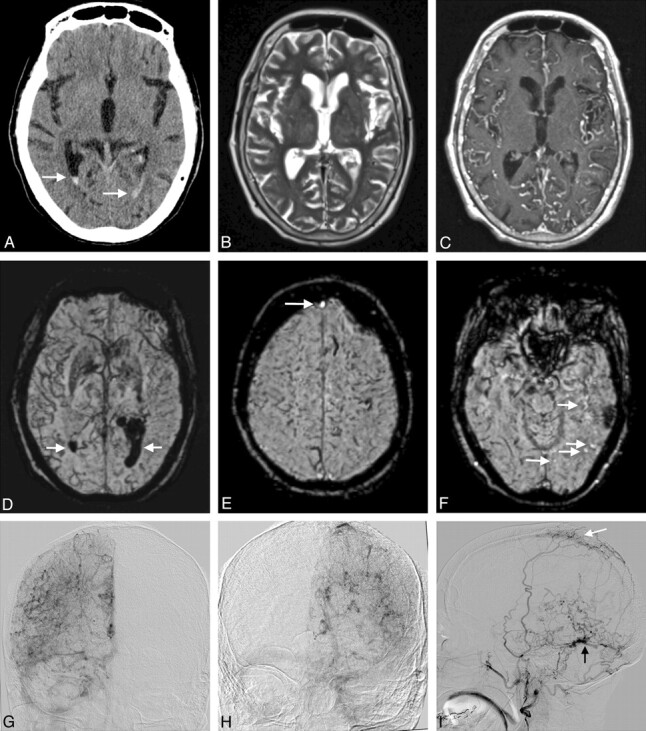
Multifocal DAVF (Borden type II and III) in an 86-year-old man presenting with aphasia (patient 2). A, Unenhanced CT scan demonstrates acute intraventricular hemorrhage (arrows). B, T2-weighted image shows a few slightly prominent leptomeningeal vessels. C, T1-weighted postgadolinium image better demonstrates the increased number of tortuous leptomeningeal vessels within both hemispheres. There are also a few tortuous medullary vessels traversing the brain parenchyma. D, mIP obtained from SWI images reveals markedly increased leptomeningeal and medullary hypointense veins affecting more severely the right hemisphere (severe PPP). Intraventricular hemorrhage is also identified (arrows). E and F, SWI images depict the hyperintensity in the anterior aspect of the superior sagittal sinus, corresponding to retrograde drainage on DSA (arrow in E). A few hyperintense veins corresponding to CVR in the vicinity of this Borden III fistula (not shown) are also identified (arrows in F). G and H, AP projections of the right and left ICA angiograms obtained in the venous phase. A severe PPP is seen bilaterally, worse on the right side, similar to the findings on SWI. The left transverse and sigmoid sinuses are occluded. I, Lateral projection of a left external carotid artery angiogram in the late arterial phase. Two DAVFs are identified, 1 located in the wall of the occluded left transverse sinus (black arrow) draining directly in cortical veins and another draining into the superior sagittal sinus (white arrow). Retrograde filling of the anterior part of the superior sagittal sinus is present, while the posterior part of the superior sagittal sinus was occluded (not shown). The extent of CVR is more extensive on DSA than depicted on SWI.
