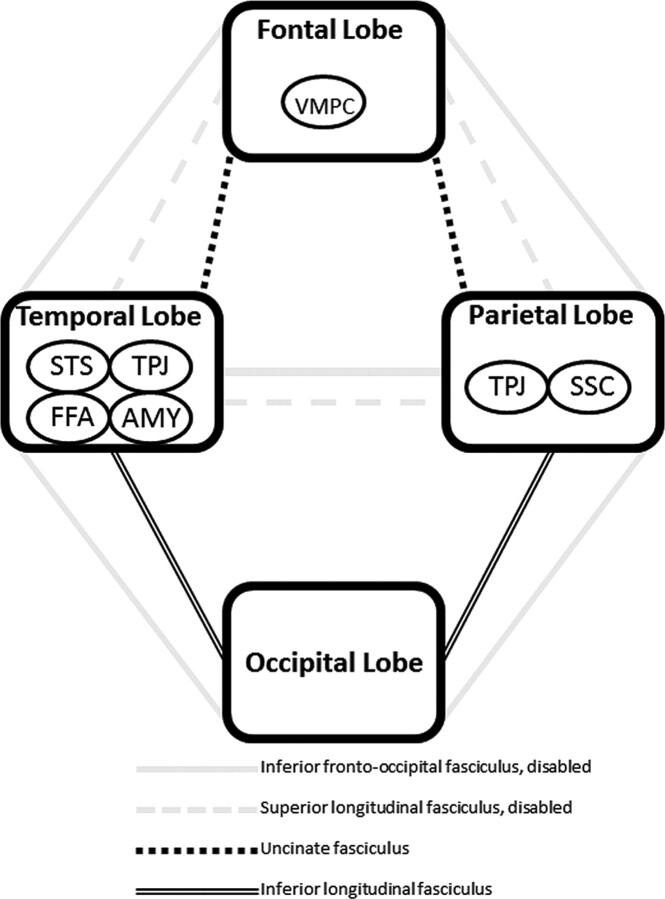
Fig 3.
Schematic diagram illustrating how the inferior fronto-occipital and superior longitudinal fasciculi might account for the social disability that characterizes autism. Disability of major pathways connecting the modules of the social brain causes reliance on smaller tracts leading to inefficient corticocortical communication. Whether any social information processing is possible depends on how severely impaired the major pathways are and whether alternative pathways are available. Abbreviations indicate modules of social information processing.