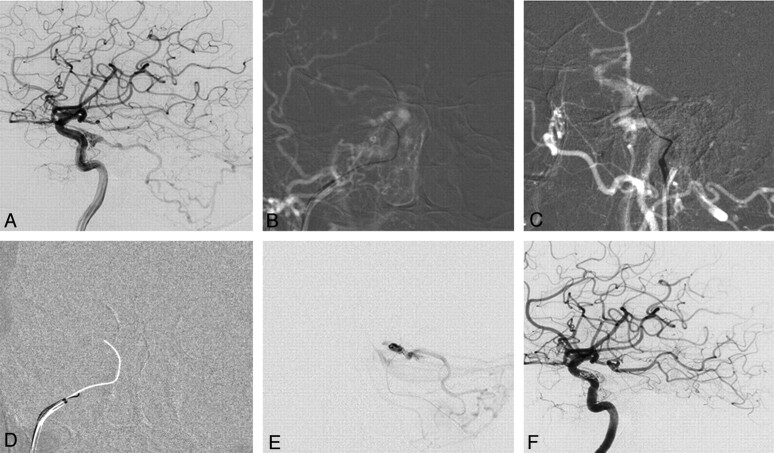
Fig 1.
DAVF of the cavernous sinus with reflux into the posterior fossa. A 76-year-old woman presented with right-sided chemosis and diplopia. A, Right internal carotid angiogram shows a DAVF at the cavernous sinus fed by cavernous branches and the meningeohypophyseal artery of the ICA with marked posterior fossa reflux. There is no flow visible into the IPS. B and C, Following an arterial roadmap, AP view (B) and lateral view (C), the guiding catheter is oriented superiorly, medially, and anteriority toward the presumed origin of the IPS. A 00.35-inch guidewire is used to reopen the occluded IPS by gentle rotation and is advanced through the occluded sinus under roadmap guidance. D, Once access is gained with the guidewire as demonstrated by the arterial roadmap, a blank roadmap is initiated, and the guidewire is removed, and a track is left for the microcatheter to enter the cavernous sinus. E, The location of the microcatheter is checked by a careful contrast injection before coil embolization to demonstrate the exact origin of the cortical venous reflux and to verify that the right compartment is coiled. F, Right internal carotid angiogram following embolization demonstrates complete obliteration of the DAVF.