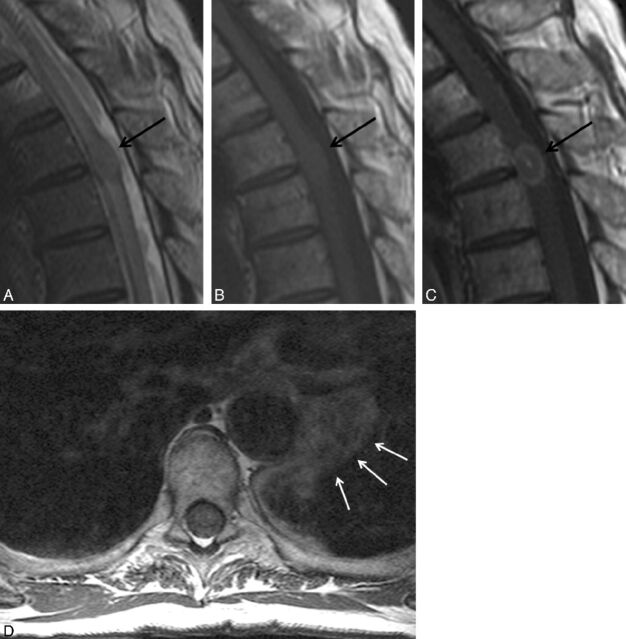
Fig 2.
Typical solitary intramedullary spinal cord metastasis, with visualization of primary tumor. A 66-year-old man presented with 6 weeks of paresthesias, bladder dysfunction, lower extremity weakness, and pain. Thoracic spine sagittal T2-weighted (A), sagittal T1-weighted (B), postcontrast sagittal T1-weighted (C), and axial T1-weighted (D) images are shown. A T2 hyperintense, expansile intramedullary cord lesion (arrow) is associated with a large amount of cord T2 hyperintensity (A). The mass is isointense on T1-weighted images (arrow in B) and enhances heterogeneously (arrow in C). Also noted is a left hilar lung mass (arrows in D), which was further evaluated with chest CT imaging (not shown). This hilar mass was pathologically proved to be a grade 4 undifferentiated small-cell lung carcinoma. Visualization on MR imaging of the primary tumor/non-CNS metastases and/or other spinal/CNS (non–spinal cord) metastases was common in this series.