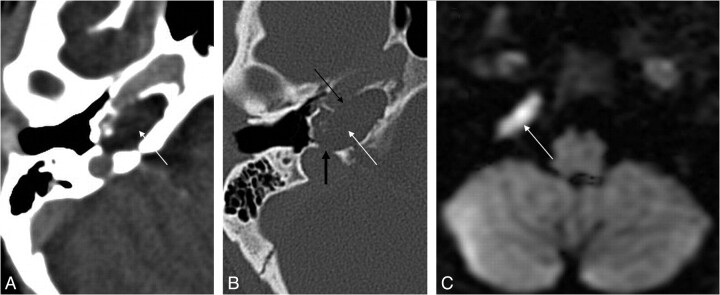
Fig 2.
Cholesteatoma of the petrous apex. Contrast-enhanced HRCT scans with a soft-tissue window (A) and a bone window (B) show an oval well-delineated, nonenhancing lesion (white arrows) with erosion of the posterior wall of the pyramidal segment of the internal carotid artery (thin black arrow) and the anterior wall of the jugular bulb (thick black arrow). C, DWI demonstrates diffusion restriction in the lesion (white arrow), supporting the diagnosis of a cholesteatoma.