Fig 2.
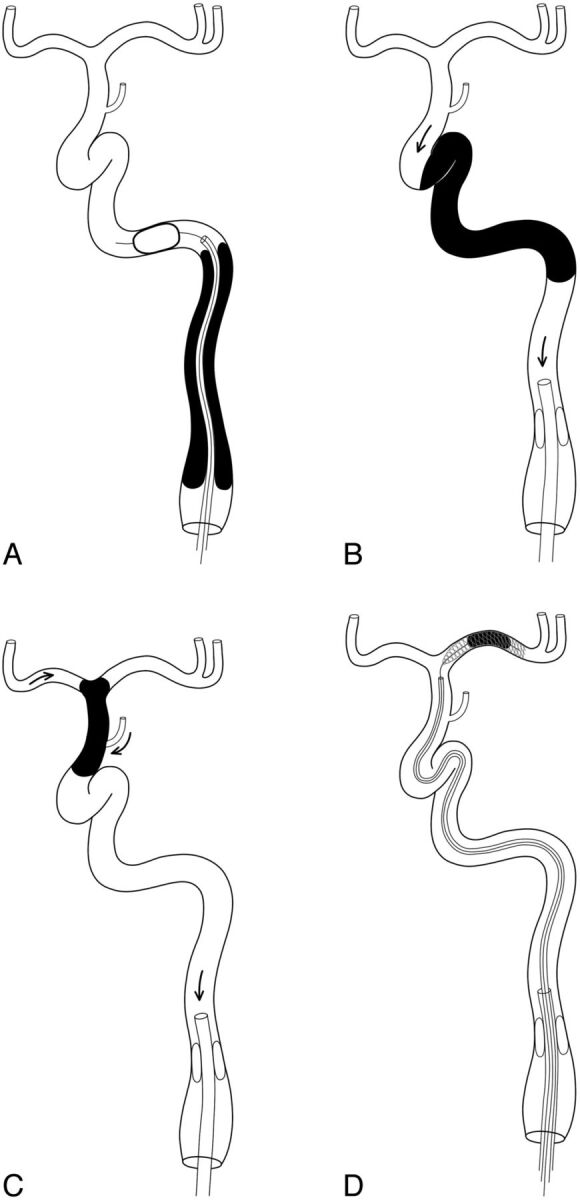
Schematic diagrams showing the protective flow arrest methods in each occluded level. A, A distal balloon was deployed beyond the bulb-cervical occlusion through a 4F catheter. Proximal balloons may be used together. Proximal flow arrest may be achieved by a proximal balloon catheter for petrocavernous (B) and supraclinoid-terminal (C) occlusions. Arrows in B and C are the flow direction when a negative pressure is applied by aspiration. There are 2 sources (the A1 and the posterior communicating artery) of the expected collateral channel in the supraclinoid-terminal segment. A fragmented or additional clot in the intracranial artery is subsequently retrieved by a stent retriever under proximal balloon protection (D).
