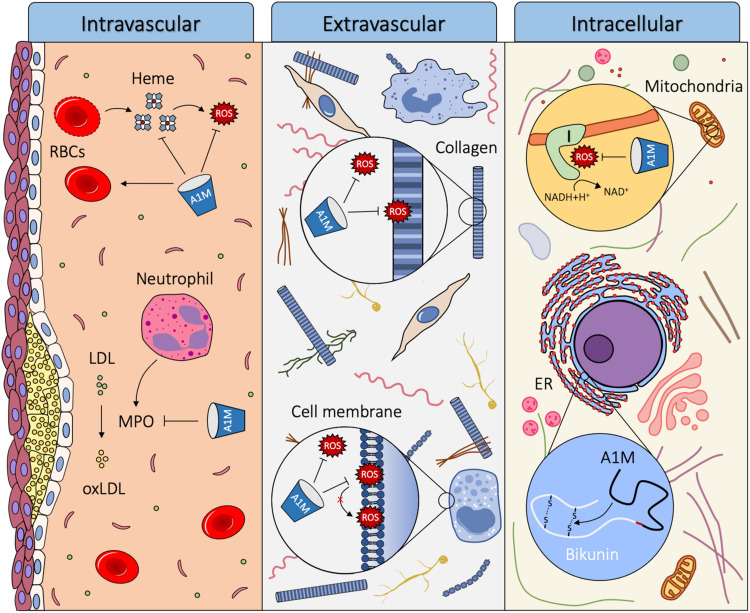
FIGURE 5.
Proposed biological roles of A1M. Using its heme binding, radical scavenging and reductase activity, A1M can act as a housekeeping protein in three different compartments of the body: intravascular, extravascular and intracellular. Intravascularly, A1M acts a stabilizer of red blood cells, it reduces damage from hemolytic events by binding heme and reducing Hb and it inhibits oxidation of LDL by MPO. Extravascularly, A1M protects tissues, cells and macromolecules from oxidative insults, including reducing oxidation products formed on ECM structures and lipid peroxidation of cell membranes. Intracellularly, A1M is bound to Complex I of the respiratory chain in the mitochondria where it may have a radical scavenging function and preserves ATP-production. A1M also acts as a chaperone during the folding of bikunin in the ER.