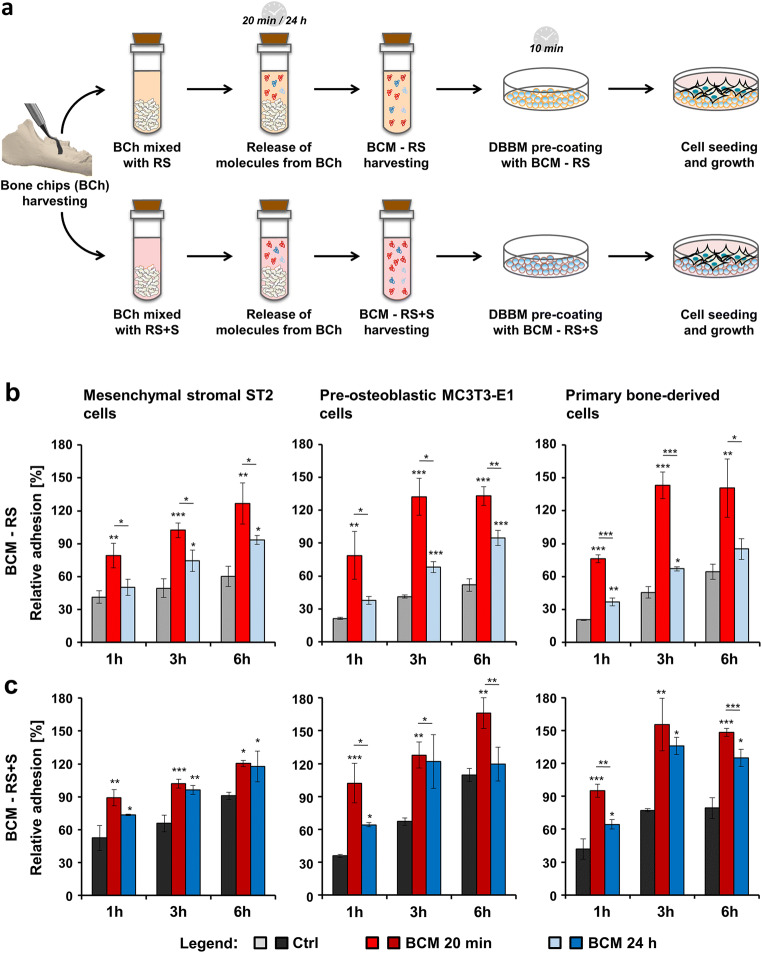
Fig. 1.
Increased adhesive properties of bone-related cell cultures grown on BCM-coated DBBM. a Schematic representation of the experimental set-up utilized throughout the study. The following steps are illustrated: (1) harvesting of cortical bone chips (BCh) from the buccal side of fresh pig mandibles using a bone scraper; (2) mixing of the BCh with extracting solutions consisting of Ringer’s solution (RS) or a 1:1 mixture of Ringer’s solution and autologous serum (RS + S); (3) incubation of the resulting mixtures for 20 min or 24 h during which time release of molecules from the BCh occurs; (4) harvesting of two types of bone-conditioned medium (BCM) labeled as BCM-RS and BCM-RS + S; (5) coating of deproteinized bovine bone mineral (DBBM) with the respective BCM preparations for 10 min prior to (6) cell seeding and growth. b, c Adhesion rate of ST2, MC3T3-E1, and primary bone–derived cells plated on DBBM coated with BCM-RS (b) or BCM-RS + S (c) prepared within 20 min or 24 h each. Controls (Ctrl) represent cells of each cell type seeded on BCM-free DBBM hydrated with RS or RS + S. Adhesion rates were assessed by crystal violet assay at 1, 3, and 6 h. Experimental values were normalized to the values obtained for the total number of seeded control cells, taken as 100% adhesion. Means ± SD from three independent experiments and significant differences to control cells at each time point unless otherwise indicated, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 are shown