Fig 1.
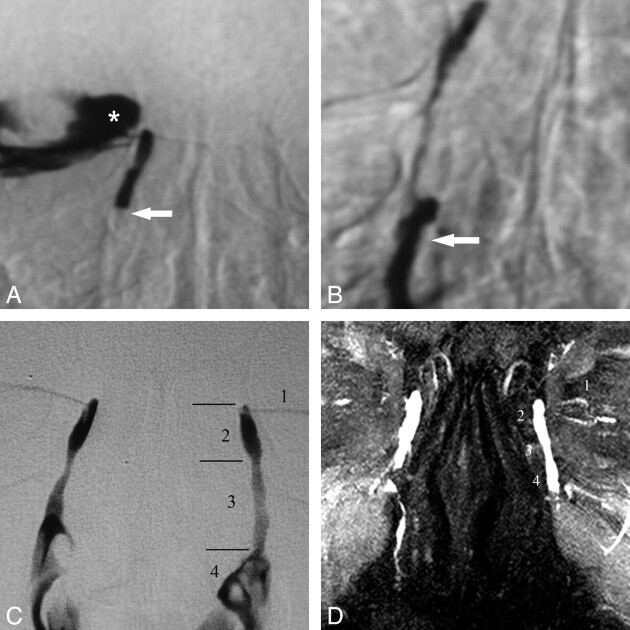
DS and MR DCG 12-year follow-up after balloon DCG in an asymptomatic patient. A, DS DCG reveals occlusion of the distal NLD (arrow) and reflux of iodinated contrast material to the conjunctival sac (asterisk). B, DS DCG immediately after transluminal balloon dilation shows passage of the contrast media to the inferior meatus of the nasal cavity (arrow). Note that there is no reflux to the conjunctival sac after successful balloon DCG. C, Twelve-year DS-DCG follow-up with bilateral simultaneous contrast media injection reveals a completely normal LDS. The anatomic regions of the normal left LDS are the following: 1) inferior canaliculus, 2) lacrimal sac, 3) NLD, and 4) contrast media in the nasal cavity. D, Bilateral topical contrast-enhanced coronal MIP DCG image from 3D FSPGR sequence demonstrates patency of the LDSs both on the intervened right side and normal left side. 1 indicates the canaliculi; 2, lacrimal sac; 3, nasolacrimal duct; 4, contrast media in the nasal cavity.