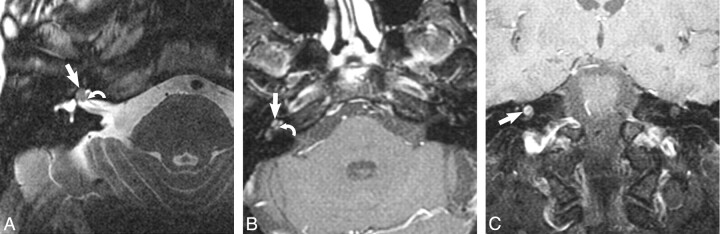
Fig 5.
Transmodiolar schwannoma. A, Axial high-resolution FSE T2-weighted MR image (4000 ms/102 ms/6 [TR/TE/NEX]) at the level of the cochlea reveals a hypointense filling defect within the cochlea (arrow), replacing the normal hyperintense CSF signal intensity, representing the transmodiolar schwannoma. Note the extension through the modiolus and cochlear nerve canal (curved arrow) into the IAC. B, Axial enhanced T1-weighted MR image (800 ms/72 ms/2 [TR/TE/NEX]) at the level of the cochlea reveals a homogeneously enhancing mass within the cochlea (arrow) with extension through the modiolus and cochlear nerve canal to involve the IAC fundus (curved arrow). C, Coronal enhanced T1-weighted MR image (800 ms/72 ms/2 [TR/TE/NEX]) at the level of the cochlea reveals a homogeneously enhancing mass in the turns of the cochlea (arrow), representing the transmodiolar schwannoma.