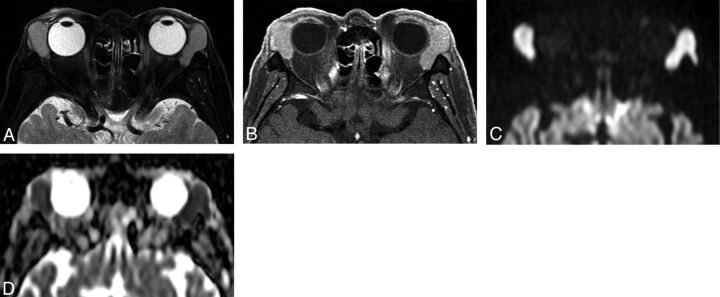
Fig 3.
Orbital lymphoma (mantle cell lymphoma) in a 71-year-old man. A, Transverse fat-saturated T2-weighted image; B, transverse fat-saturated postcontrast T1-weighted image; C, transverse DWI; and D, ADC map. The lesions involve the bilateral lacrimal glands, appear isointense compared with the brain cortex on fat-saturated T2-weighted image (A), and show homogeneous contrast enhancement, similar that of the extraocular muscles (B). The lesions are strongly hyperintense on the DWI (C) and hypointense on the ADC map (D). Lesion ADC and CER were 0.47/0.48 (right/left) ×10−3 mm2/s and 1.49/1.46 (right/left), respectively. The low ADC and CER values could suggest orbital lymphoma though the imaging features are similar to that of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease (Fig 2).