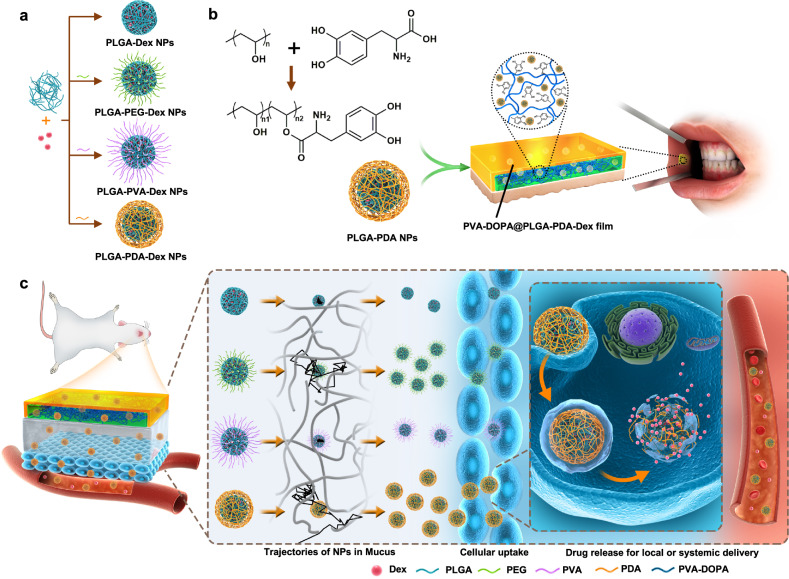
Fig. 1. Synthesis and biomedical application of PVA-DOPA@NPs-Dex mucoadhesive film.
a Illustrations displaying the method used to assemble core-shell PLGA NPs with different surface modifications. b Schematic presentation of the fabrication of the PVA-DOPA@NPs-Dex film with enhanced mucoadhesion for buccal drug delivery. c Schematic diagram of the application of PVA-DOPA@NPs-Dex film to the rat buccal mucosa and the process by which the NPs to sequentially permeate the mucus layer and epithelial cells. PDA-coated PLGA NPs could overcome both barriers rapidly and subsequently release drugs for local or systemic delivery. NPs: nanoparticles, Dex: dexamethasone, PLGA: poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid), PEG: poly(ethylene glycol), PVA: poly(vinyl alcohol), PDA: polydopamine, DOPA: 3,4-dihydroxy-D-phenylalanine.