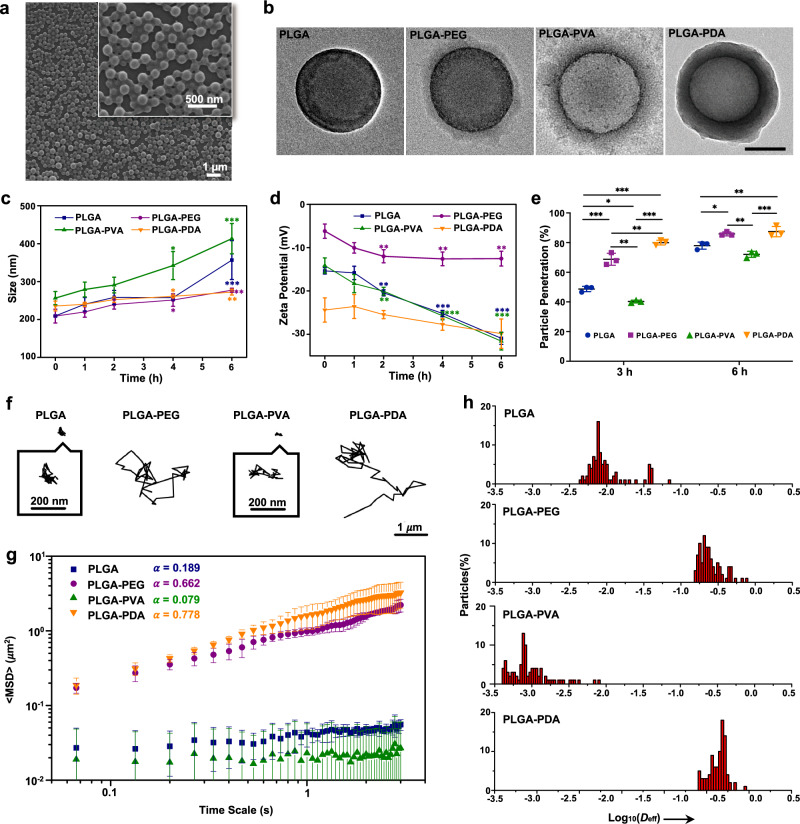
Fig. 4. Characterization and mucus-penetrating properties of NPs in vitro.
a SEM image of PLGA NPs. b TEM images of PLGA, PLGA-PEG, PLGA-PVA, and PLGA-PDA NPs. PLGA: poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid), PEG: poly(ethylene glycol), PVA: poly(vinyl alcohol), PDA: polydopamine. Scale bar: 100 nm. c Variation in the particle size of different NPs-Mucin mixtures as a function of time. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 vs value at 0 h. d Variation in the zeta potential of different NPs-Mucin mixtures as a function of time. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 vs value at 0 h. e Percentage of NPs that penetrated across the mucus layer in a Transwell assay after 3 h and 6 h. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. f Representative trajectories of different NPs in mucus. g MSD (mean squared displacement) values as a function of time scale for different NPs in mucus. h Distributions of the logarithms of individual particle effective diffusivities (Deff) values at a time scale of 1 s. All data are Mean ± S.D. n = 3 independent samples per group. Statistics was calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-test. Exact P values are given in the Source Data file. Source data are provided as a Source data file.