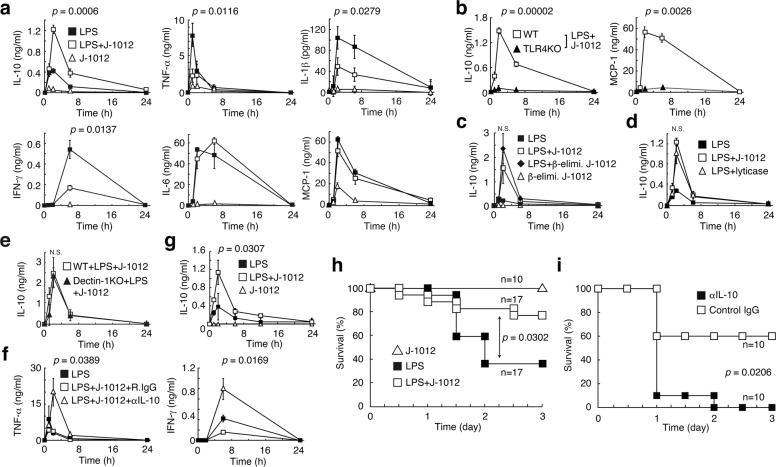
Fig. 1. N-glycan of C. albicans up-regulates IL-10 production and improves mouse septic responses with LPS.
a, b Serum cytokines after i.v. injection with a low dose of LPS (15 μg/20 g mouse weight) and J-1012 N-glycan (400 μg N-glycan/20 g mouse weight) in WT (a) or TLR4KO mice (b). c, d Serum IL-10 after i.v. injection with J-1012 N-glycan purified after β-elimination (c) or J-1012 N-glycan treated by lyticase in WT mice (d). e Effects of deficient of Dectin-1 on serum IL-10. f Effects of anti-IL-10 on serum cytokines. g Serum IL-10 after i.p. injection with a lethal dose (100 μg/20 g mouse weight) of LPS and J-1012 N-glycan. h, i Survival rates of mice after i.p. injection with J-1012 N-glycan and the high dose of LPS in the absence (h) or the presence (i) of mAbs, as indicated. These experiments were repeated twice, and compiled results are shown. a–g Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3) (a, c–g), (n = 6) (b) and are representative of at least two independent experiments. Statistical analyses were performed between LPS and LPS + J-1012 (a, g), LPS + J-1012 and LPS + J-1012 with β-elimination (c), LPS + J-1012 and LPS + J-1012 with lyticase (d), LPS + J-1012 + R.IgG and LPS + J-1012 + αIL-10 (f). p value at the peak point of cytokine production was determined by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. N.S., not significant (p > 0.05). h, i p value was determined by the Wilcoxon test.