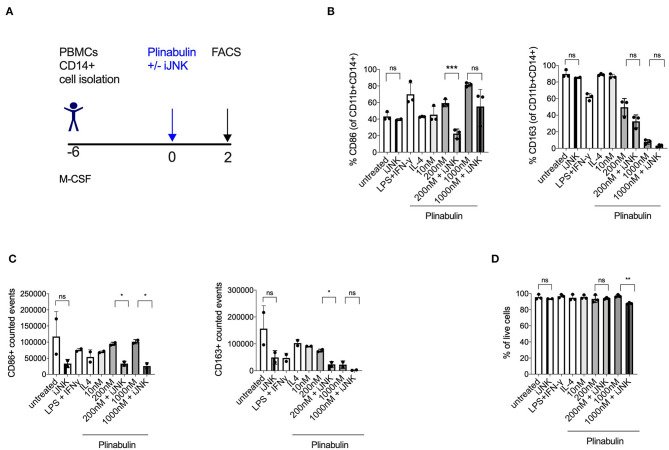
Figure 4.
Plinabulin-induced M1 polarization is JNK-dependent. (A) Experimental outline of macrophage generation from healthy donor PBMCs and treatment with plinabulin at indicated doses or controls in the presence of a JNK inhibitor SP600125 (iJNK, 20 μM). (B) Percentage of CD86+ (left) or CD163+ (right) cells out of CD11b+ CD14+ human macrophages, treated with plinabulin or control conditions in the presence or absence of a JNK inhibitor. (C) CD86+ (left) or CD163+ (right) events out of CD11b+ CD14+ human macrophages, treated with plinabulin or control conditions in the presence or absence of a JNK inhibitor, calculated using counting beads on flow cytometry. (D) Percentage of live cells (cells negative for the live cell exclusion dye) out of total human macrophages, treated with plinabulin or control conditions, measured by flow cytometry. (B–D) Statistical significance was determined by Kolmogorov-Smirnov t-test between the indicated groups. P-values indicated on the graphs: ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Error bars show SD. Data are derived from two independent experiments: one with two individual donors and one with sample pooled from two donors.