Fig 1.
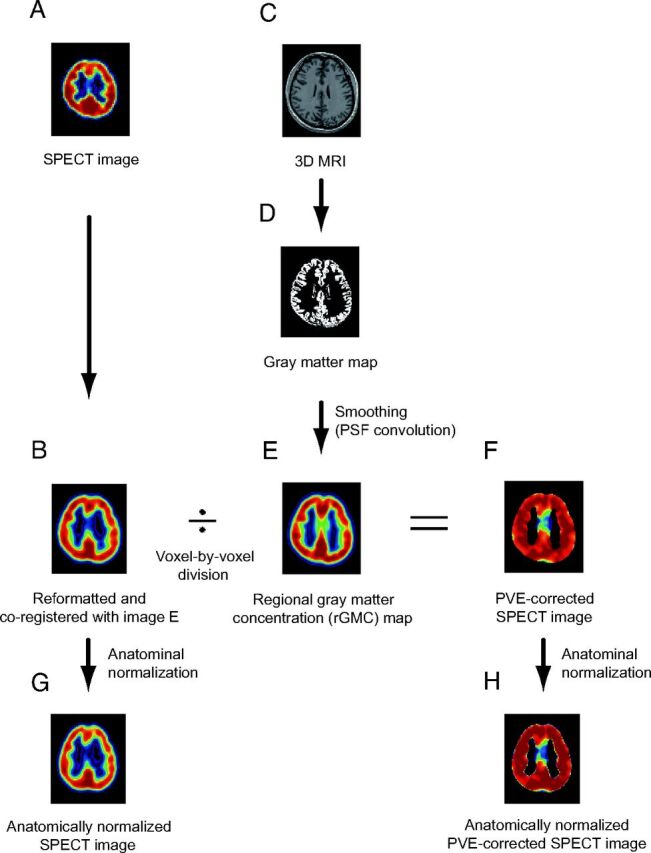
A, I-123 iomazenil SPECT image. B, Automatic coregistration of the I-123 SPECT image with the MR image via smoothed gray matter maps. The maps are simultaneously reformatted to a matrix that is the same size as the referenced smoothed gray matter map. C, 3D MR image obtained before surgery. D, MR image segmented into Bayesian probability maps showing 3 tissue classes (gray matter, white matter, and CSF maps). E, The gray matter map convoluted with the PSF, which is assumed to be the same as the PSF of the SPECT scanner. The resultant image is subsequently referred to as the rGMC map. F, Smoothed gray matter map masked with a threshold set to 35% of the maximum voxel value. The coregistered I-123 SPECT image is divided by using the masked smoothed gray matter map on a voxel-by-voxel basis. G, Image (B) anatomically normalized by the spatial normalization matrices generated in the segmentation process. H, Image (F) anatomically normalized in the same manner as in image G.
