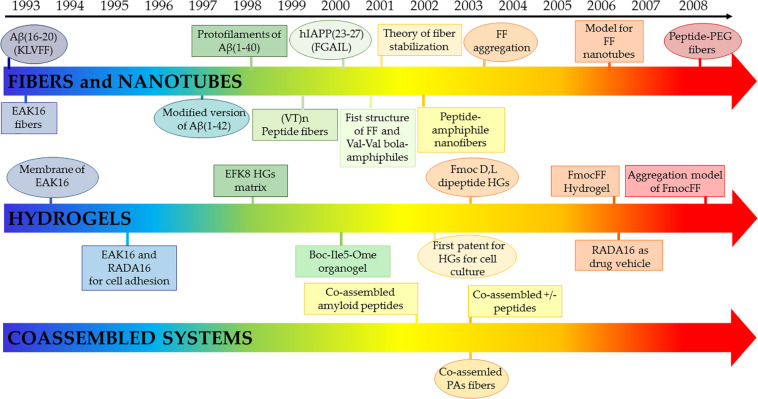
FIGURE 7.
Selected early milestones on self-assembling peptides assuming cross-β structures as elements for fibers and nanotubes, hydrogels and co-assembled biomaterials. Reference for each group are reported following. Fibers and nanotubes: Aβ(16-20) (KLVFF) (Hilbich et al., 1992); EAK16 fibers (Zhang et al., 1993a); modified version of Aβ(1-42) (Seilheimer et al., 1997); protofilaments of Aβ(1-40) (Malinchik et al., 1998); (VT)n peptide fibers (Janek et al., 1999); hIAPP(23-27) (FGAIL) (Tenidis et al., 2000); Val-Val bola-amphiphiles (Kogiso et al., 2000); theory of fiber stabilization (Nyrkova et al., 2000); first crystallographic structure of FF (Görbitz, 2001); peptide-amphiphile nanofibers (Hartgerink et al., 2002); FF aggregation (Reches and Gazit, 2003); model for FF nanotubes (Görbitz, 2006); peptide-PEG fibers (Hamley and Krysmann, 2008). Hydrogels: membranes of EAK16 (Zhang et al., 1993b); EAK16 and RADA16 for cell adhesion (Zhang et al., 1993b); EFK8 HGs matrix (Leon et al., 1998); Boc-Ile5-Ome organogel (Jayakumar et al., 2000); Fmoc D,L dipeptide HGs (Zhang et al., 2003); FmocFF Hydrogel (Mahler et al., 2006); RADA16 as drug vehicle (Nagai et al., 2006); aggregation model of Fmoc-FF (Smith et al., 2008). Co-assembled systems: co-assembled amyloid peptides (Takahashi et al., 2002); co-assemled PAs fibers (Niece et al., 2003); co-assembled ± peptides (Aggeli et al., 2003).