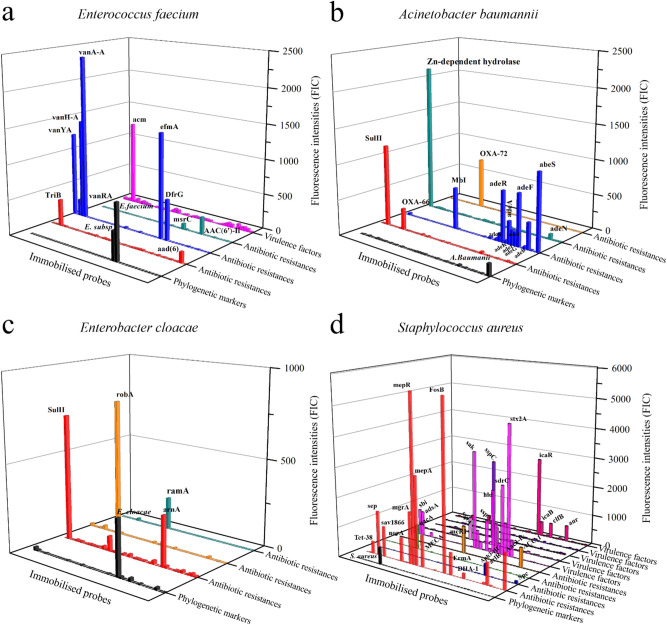
Figure 3.
Full characterisation of Enterococcus faecium (a), Acinetobacter baumannii (b), Enterococcus cloacae (c), and Staphylococcus aureus (d) isolates, comprising identification (black) via 16S rRNA genes and characterisation in terms of ABR genes (red/blue/green/orange) and VFs (magenta and related colors). The DNA of a clinical isolate carrying the specified pathogen was purified and amplified by multiplex PCRs including the primer pairs of all investigated genes. The amplification products were applied to the microarray chips along with detection oligonucleotides. If matching, the detection oligonucleotides could be ligated to the probes and subsequently detected by a standard fluorescence-based microarray scanner.