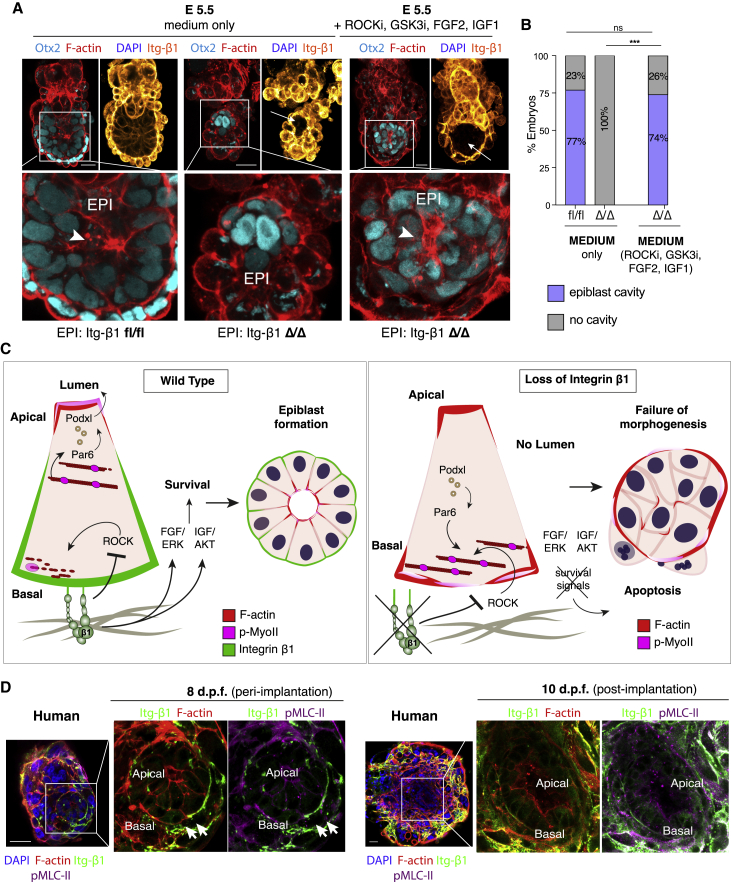
Figure 6.
In vivo rescue of survival and morphogenesis in mouse embryos and spatial segregation of integrin β1 and actomyosin in the human embryo
(A) Culture of mouse embryos from pre- to post-implantation as shown in Figure S3F: wild-type controls (Epi:fl/fl) develop into post-implantation egg-cylinders (left), mutant epiblasts deficient for integrin β1 (Epi:Δ/Δ) fail to undergo lumenogenesis and to survive during post-implantation development in normal culture conditions (center). Supplementation with ROCKi, FGF2, IGF1, and GSK3i restores lumenogenesis and survival of the epiblast compartment in integrin β1-deficient embryos (right).
(B) Quantification of the percentage of embryos undergoing lumenogenesis in wild-type and mutant embryos cultured in normal conditions compared to mutant embryos cultured in the presence of ROCKi, FGF2, IGF1, and GSK3i. Fisher’s exact test: fl/fl versus Δ/Δ ROCKi/FGF2/IGF1/GSK3i p = ns; Δ/Δ medium versus Δ/Δ ROCKi/FGF2/IGF1/GSK3i ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (number of embryos n = 26 [fl/fl], n = 16 [Δ/Δ], n = 51 [Δ/Δ, ROCKi/FGF2/IGF1/GSK3i]).
(C) Schematic summary of results. Wild-type (left): integrin β1-mediated adhesion to the basement membrane leads to suppression of actomyosin basally, allowing its apical localization. Activation of actomyosin at the apical side leads to the apical localization of PAR6 (Figure 4G) and secretion of podocalyxin vesicles and initiation of lumenogenesis (Figure 4H). Integrin β1 promotes epiblast survival via stimulation of FGF/ERK and IGF1/AKT pathways. Mutant (right): loss of integrin β1 leads to ectopic actomyosin accumulation basally. The basal actomyosin recruits PAR6 basally, which directs podocalyxin vesicles toward the basal side, preventing lumenogenesis. Loss of integrin β1 leads to apoptosis.
(D) Assessment of the localization of integrin β1 and actomyosin in human embryos at day 8 d.p.f. shows initiation of spatial segregation between the 2 complexes in a mutually exclusive manner (arrows). At 10 d.p.f., the 2 are fully segregated, with integrin β1 localizing on the basolateral domain, while actomyosin is confined on the apical side of the epiblast epithelium facing the central amniotic cavity.
Scale bars: 25 μm (A) and 50 μm (D).