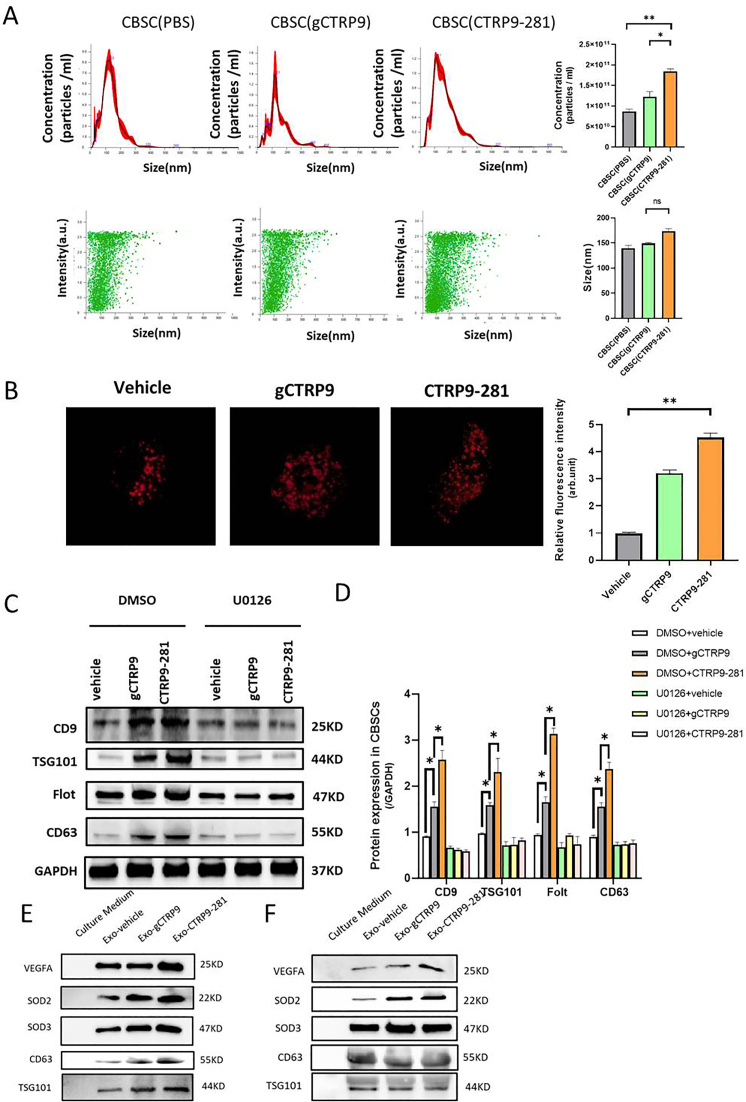
Fig. 5.
CTRP9-281 increases VEGF-enriched exosome biogenesis by CBSC. A: Nanosight test the number and size distribution of exosomes derived from the CBSCs after PBS, gCTRP9 (2 μg/ml) and CTRP9-281 (2 μg/ml) treatment for 24 h n = 10–12/group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. B: gCTRP9 and CTRP9-281 increase the exosome biogenesis as evidenced by increased multivesicular body (MVBs) formation. CBSC were transfected with pCS2 hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate (HRS)-RFP plasmid. Cells were treated with vehicle, gCTRP9 or CTRP9-281 for 24 h. The HRS-RFP positive MVBs were significantly increased in CBSCs treatment with gCTRP9 and CTRP9-281 (n ≥ 5, One-Way ANOVA, **p < 0.01). C/D: Western blot showed the Exosome marker protein expression in CBSC after gCTRP9 (2 μg/ml) and CTRP9-281(2 μg/ml) treatment for 24 h. U0126 (an ERK1/2 activation inhibitor) blocked CTRP9-281 and gCTRP9-induced exosome biogenesis (U0126: 10 μM 2 h before CTRP9-281 treatment; n = 4–5/group). E: Western blot analysis of VEGFA, SOD2 and SOD3 expression in exosomes isolated from vehicle, gCTRP9 and CTRP9-281 treated CBSC (1 × 106/well). n = 8/group, *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle. F. Western blot analysis of VEGFA, SOD2 and SOD3 expression in equal number of exosomes. n = 6/group.