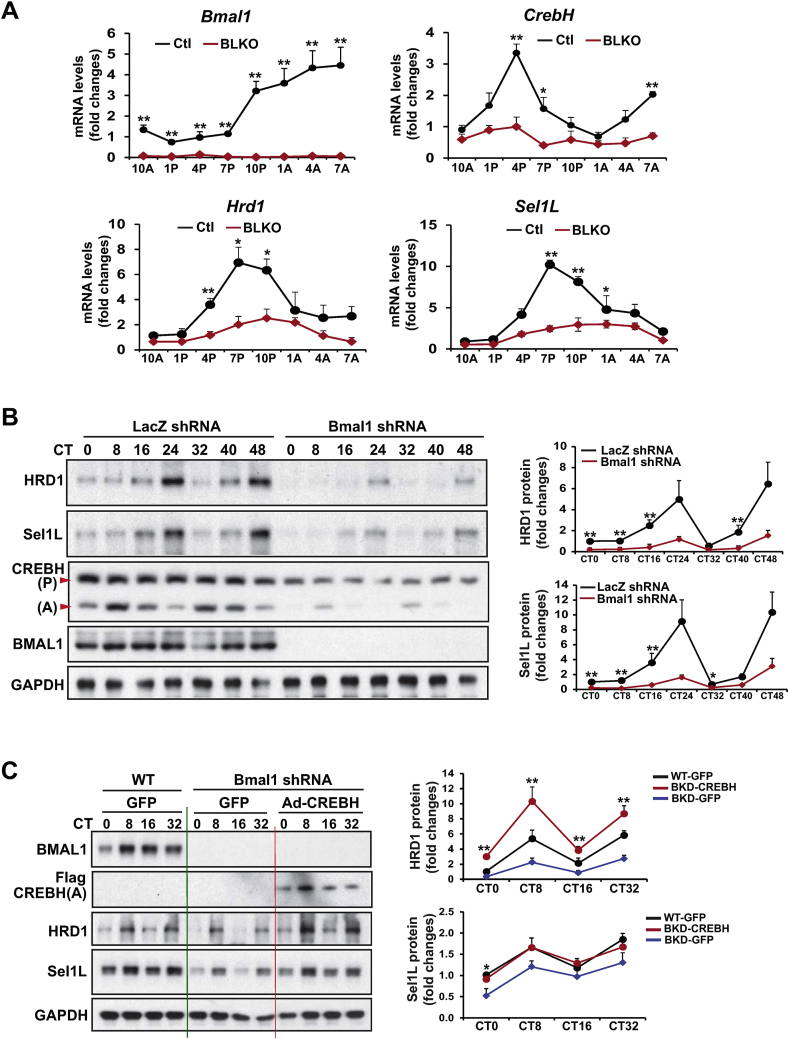
Figure 3.
BMAL1 controls circadian rhythmic expression of HRD1/Sel1L in the liver through regulating CREBH. (A) Rhythmic expression levels of Bmal1, CrebH, Hrd1, and Sel1L genes in the livers of Bmal1 LKO and fl/fl control mice across a 24-h circadian cycle. The liver total RNAs were prepared from the mice collected every 3 h during a 24-h circadian period. The mRNA expression levels were determined by qPCR. Fold changes in mRNA levels were determined by comparison to levels in one of the control mice at 10 AM. Data represent means ± SEM (n = 3–4 mice/genotype/time point). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01. (B) Western blot analysis of HRD1, Sel1L, CREBH, BMAL1, and GAPDH protein levels in Bmal1 knockdown and control primary hepatocytes during a 48-h circadian cycle. Mouse primary hepatocytes were infected with adenovirus expressing Bmal1 shRNA or control LacZ shRNA for 24 h before being subjected to horse serum shock for circadian synchronization. Cell lysates were collected at 8-h intervals during a 48-h circadian cycle for Western blot analysis to determine levels of HRD1, Sel1L, BMAL1, and GAPDH. The graphs show the rhythmic fold changes of HRD1 and Sel1L proteins in Bmal1 knockdown and control primary hepatocytes during the circadian cycle. Protein signals, determined by Western blot densitometry, were normalized to that of GAPDH. Fold change of the normalized HRD1 or Sel1L protein levels at each circadian time point was calculated by comparing to the level in control cells at the starting circadian time. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 experimental replicates). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01. CT, circadian time. (C) Western blot analyses of BMAL1, CREBH, HRD1, Sel1L, and GAPDH in Bmal1-knockdown and WT control mouse primary hepatocytes expressing the activated CREBH or GFP control under the circadian clock. Mouse primary hepatocytes were infected with Ad expressing Bmal1 shRNA, the activated form of CREBH (Flag-tagged), or GFP before being subjected to horse serum shock for circadian synchronization. Primary hepatocytes from WT mice were infected with Ad expressing GFP (WT-GFP) were included as a control. Cell lysates were collected throughout a 32-h circadian cycle for Western blot analyses. The graphs show the rhythmic fold changes of HRD1 and Sel1L protein levels, determined by Western blot densitometry, in Bmal1-knockdown and WT control hepatocytes expressing CREBH or GFP control. Fold change of normalized protein levels at each circadian time point was calculated by comparing to the level in control cells at the starting circadian time. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 experimental replicates). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01.