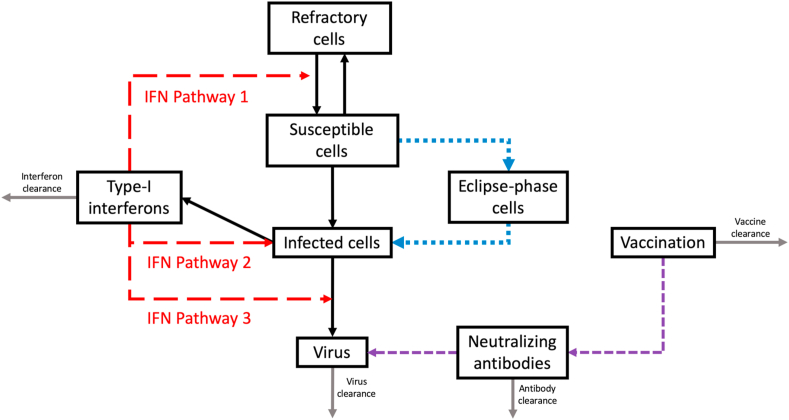
Fig. 1.
A simplified model schematic representing three type-I IFN pathways examined in this study. 1) Induction of a refractory cell state, 2) activation of Natural Killer (NK) cells leading to destruction of infected cells, and 3) reduction of virus replication in infected cells (type-I IFN sensitivity). An eclipse phase was also tested in the model in addition to account for the effect of a cellular latent period (blue dotted lines). The effect of vaccination on the production of neutralizing antibodies was also examined (purple dashed lines).