Figure 6.
The complete effects of GVS in the in vivo model including hair cell adaptation
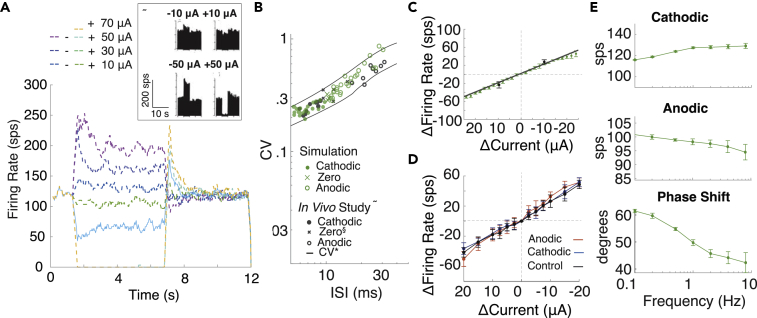
(A) Firing range induced with current steps from –50 μA to 70 μA, showing adaptation and axonal response that matches in vivo experimental results (box).
(B) The CV versus ISI associated with GVS stimulation using the model (green) compared with the CV ISI relationship in the original paper (black), which indicates cathodic stimulation (filled circle), anodic stimulation (open circle), and natural head rotation (x's).
(C) The change in firing rate with cathodic current steps at slope of 2.5 sps/μA (black) as in the experimental results.
(D) The change in firing rate with current steps up to ±20 from (A)10, +10, and 0 μA current baselines across five repetitions.
(E) The change in firing rate to cathodic and anodic portions of sine waves of 10 μA amplitude and the phase shift to frequencies from 0.1 to 10 Hz. All statistical data are presented as mean ± std.