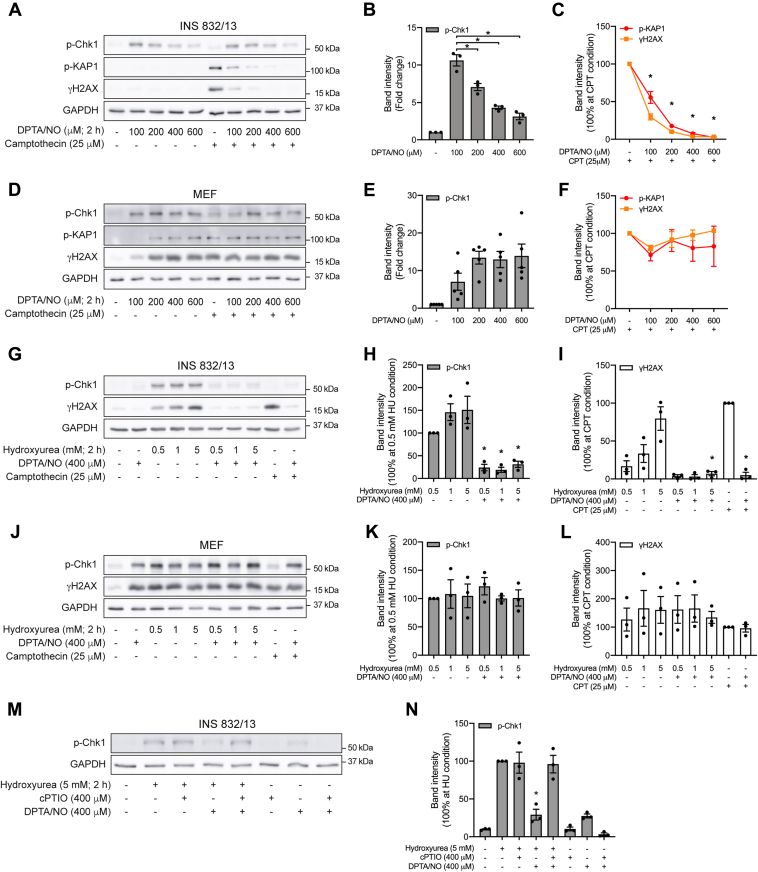
Figure 3.
Cell type selective inhibition of ATR signaling by nitric oxide. INS 832/13 cells (A–C and G–I) and MEF (D–F and J–L) were treated with the indicated concentrations of DPTA/NO, hydroxyurea, or camptothecin for 2 h alone or in combination, or INS 832/13 cells (M and N) were treated with hydroxyurea in the presence or absence of cPTIO or DPTA/NO for 2 h. The phosphorylation of Chk1, KAP1, and H2AX was determined by Western blot analysis (A, D, G, J, and M) and quantified by densitometry (B, C, E, F, H, I, K, L, and N). GAPDH levels were determined to control for protein loading. For densitometry in B and E, all conditions were normalized to the untreated group and set at one; in C, F, H, I, K, L, and N, all conditions were normalized to hydroxyurea- or camptothecin-treated groups and set at 100%. Results are representative (A, D, G, J, and M) or the average ± SEM (B, C, E, F, H, I, K, L, and N) of two to five independent experiments. Statistically significant decrease in Chk1 phosphorylation (B) and inhibition of camptothecin-induced phosphorylation of KAP1 and H2AX (C), hydroxyurea-induced phosphorylation of Chk1 (H and N), and hydroxyurea- or camptothecin-induced γH2AX formation (I) are indicated (∗p < 0.05). ATR, ataxia–telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein; Chk1, checkpoint kinase 1; cPTIO, 2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1H-imidazolyl-1-oxy-3-oxide; DPTA/NO, (Z)-1-[N-(3-aminopropyl)-N-(3-ammoniopropyl)amino]diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate; H2AX, H2A histone family member X; KAP1, Krüppel-associated box–associated protein 1; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblast.