Figure 8.
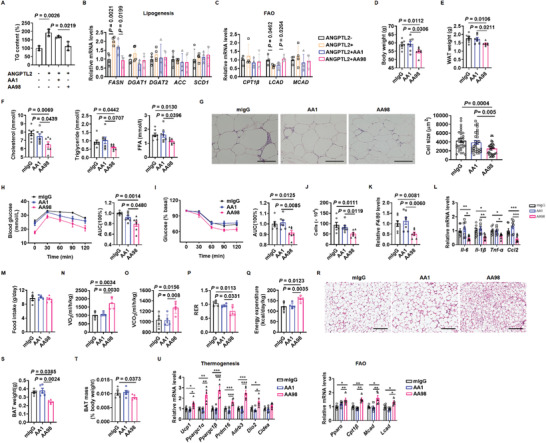
Anti‐CD146 AA98 antibody attenuates obesity development and obesity‐related inflammation. A) Triglyceride (TG) content of adipocytes differentiated from human SVF treated with ANGPTL2 or anti‐CD146 AA98 or AA1 antibodies. RT‐qPCR showing the expression of lipogenesis B) and fatty acid oxidation‐related genes C) in human adipocytes treated with ANGPTL2 or anti‐CD146 AA98 or AA1 antibodies. Body weight D) and WAT weight E) of db/db mice treated with AA98, AA1, or mIgG (n = 7 per group). F) Serum cholesterol, triglyceride, and free fatty acid (FFA) levels in db/db mice treated with AA98, AA1, or mIgG (n = 7 per group). G) Representative H&E images and quantification of adipocyte size in db/db mice treated with AA98, AA1, or mIgG. H) GTT (left) and the AUC of GTT (right) in db/db mice treated with AA98, AA1, or mIgG (n = 7 per group). I) ITT (left) and the AUC of ITT (right) in db/db mice treated with AA98, AA1, or mIgG (n = 7 per group). Macrophage number J) and macrophage gene F4/80 expression K) in the visceral fat pads of db/db mice treated with AA98, AA1, or mIgG (n = 7 each group). L) RT‐qPCR showing the expression of proinflammatory factors in visceral adipose tissue from db/db mice treated with AA98, AA1, or mIgG (n = 7 per group). M) Food intake of db/db mice treated with AA98, AA1, or mIgG (n = 5 per group). Oxygen consumption N), carbon dioxide production O), respiratory quotient P) and energy expenditure Q) of db/db mice treated with AA98, AA1, or mIgG (n = 5 per group). R) Representative H&E images of BAT from db/db mice treated with AA98, AA1, or mIgG. Scale bar, 200 µm. BAT weight S) and mass T) of db/db mice treated with AA98, AA1, or mIgG (n = 5 each group). U) RT‐qPCR showing the expression of thermogenesis and fatty acid oxidation (FAO)‐related genes in BAT from db/db mice treated with AA98, AA1, or mIgG (n = 5 per group). Data represent the mean ± SD in (A)–(C) and mean ± SEM in (D‐U). P values were determined using two‐way ANOVA in (A)–(C) and one‐way ANOVA in (D‐U). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001
