Figure 10:
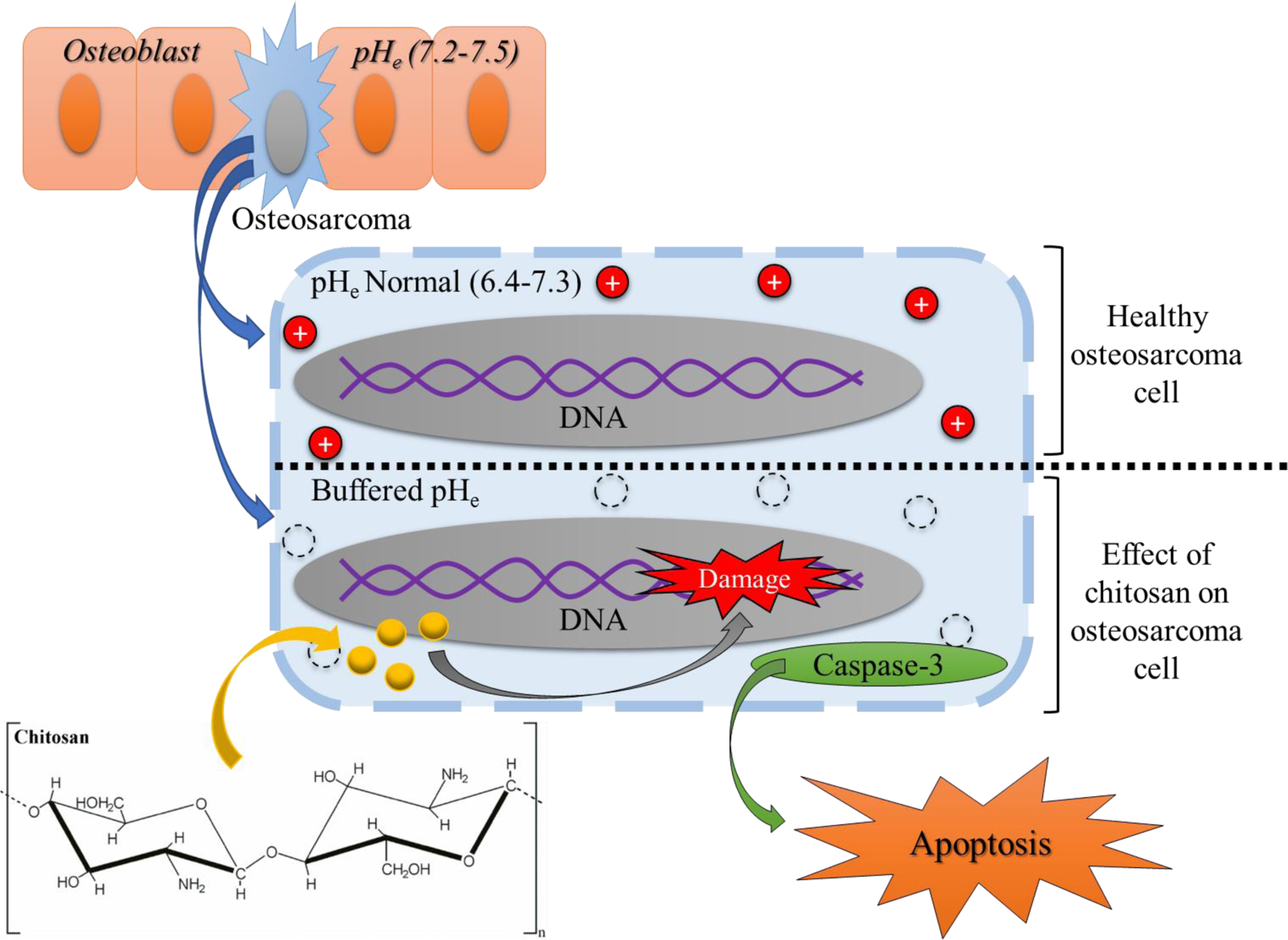
Possible mechanism of action regarding chitosan and its chemopreventative properties. Chitosan can cause deprotonation of the cell cytoplasm, buffering the pHe in the cell by the amino groups accepting protons [21]. Chitosan can also cause DNA damage and cause the activation of caspase-3 leading to cellular apoptosis [18].
