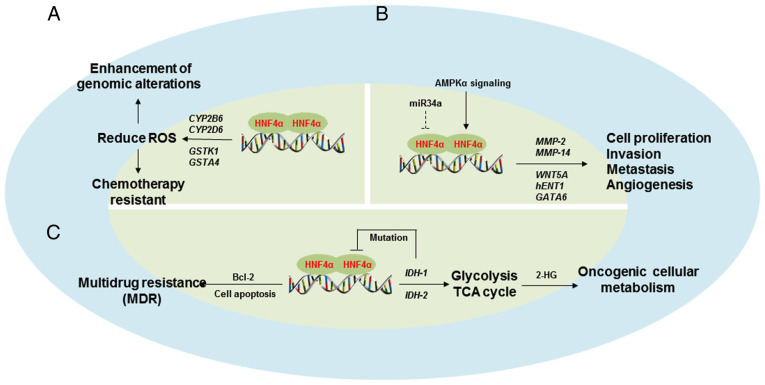
Figure 4.
Oncogenic roles of HNF4α. Schematic diagram depicting the published mechanisms of the oncogenic role of HNF4α in cancer. (A) HNF4α could reduce levels of ROS to enhance genomic alterations and chemotherapeutic-resistance of cancer cells. (B) Increased expression of HNF4α could promote cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis via increasing MMP-2 and MMP-14 expression. (C) Overexpression of HNF4α induces multidrug-resistance via Bcl-2 mediated cell apoptosis and promotes oncogenic cellular metabolism by directly targeting the IDHs related to glycolysis and TCA cycle. CYP2B6, cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily B member 6; CYP2D6, cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily D member 6; GATA6, GATA binding protein 6; GSTA4, GATA binding protein 4; GSTk1, glutathione S-transferase kappa 1; hENT1, human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1; IDH-1, isocitrate dehydrogenase 1; IDH-2, isocitrate dehydrogenase 2; MMP-14, matrix metalloproteinase 14; MMP-2, matrix metalloproteinase 2; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; WNT5A, Wnt family member 5A.