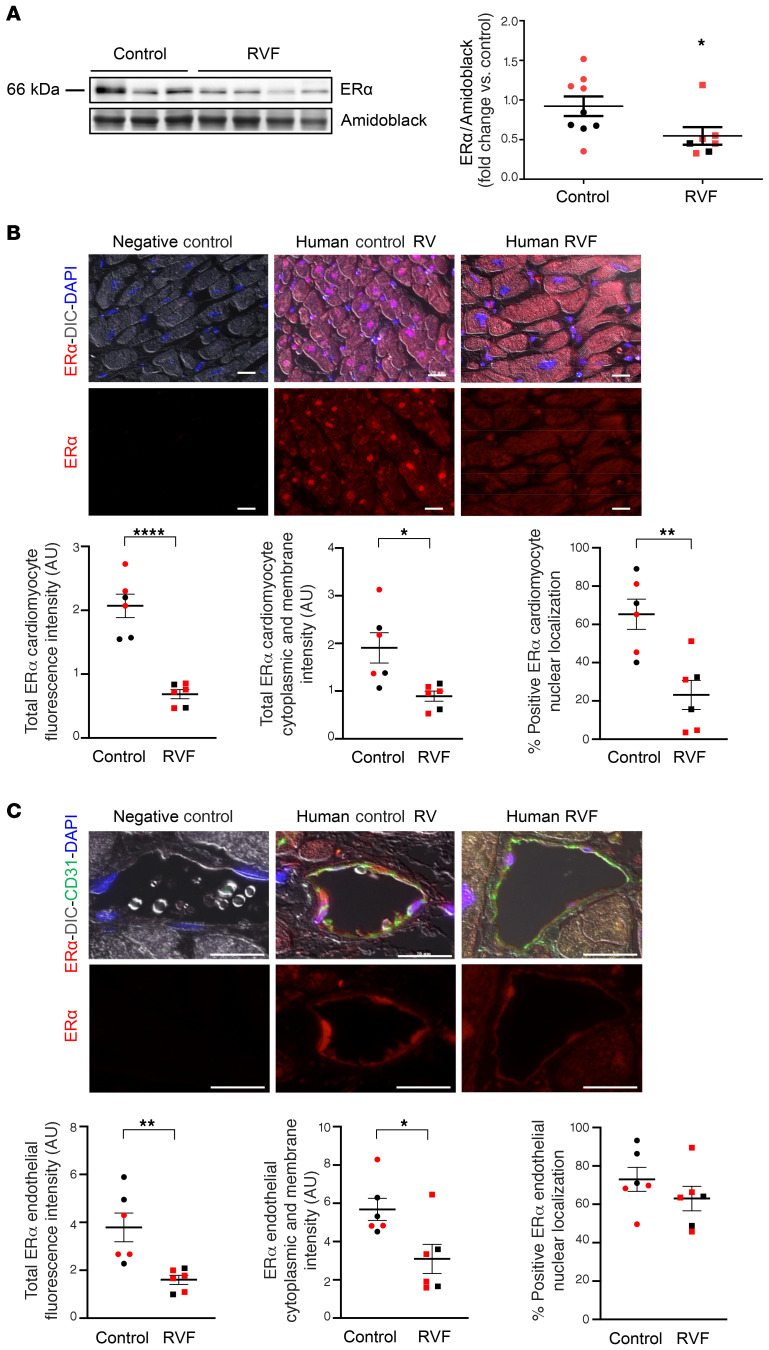
Figure 1. ER-α localizes to cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells in the human RV and is less abundant in patients with RV failure.
(A) ER-α expression in human RV measured by Western blot. Quantification by densitometry shown on right. (B) Representative immunohistochemistry images of RV cardiomyocyte ER-α expression and localization in human control RVs and RVs from patients with RV failure (RVF). Cardiomyocyte localization was established by differential interference contrast (DIC). Quantification of total ER-α fluorescence intensity, cytoplasmic and membrane fluorescence intensity (measured in AU), and nuclear localization (colocalization with DAPI) is shown in graphs. Images are at 20× magnification; scale bar: 20 μm. (C) Representative immunocytochemistry images of ER-α expression and localization in RV endothelial cells in human control RVs and RVs from patients with RVF. Endothelial cell localization was established by colocalization with CD31. Total ER-α fluorescence intensity, cytoplasmic and membrane fluorescence intensity, and nuclear localization (colocalization with DAPI) are quantified in graphs. Images are at 40×, scale bars: 20 μm. Red and black symbols in graphs represent samples from female and male patients, respectively. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 versus control by Student’s t test.