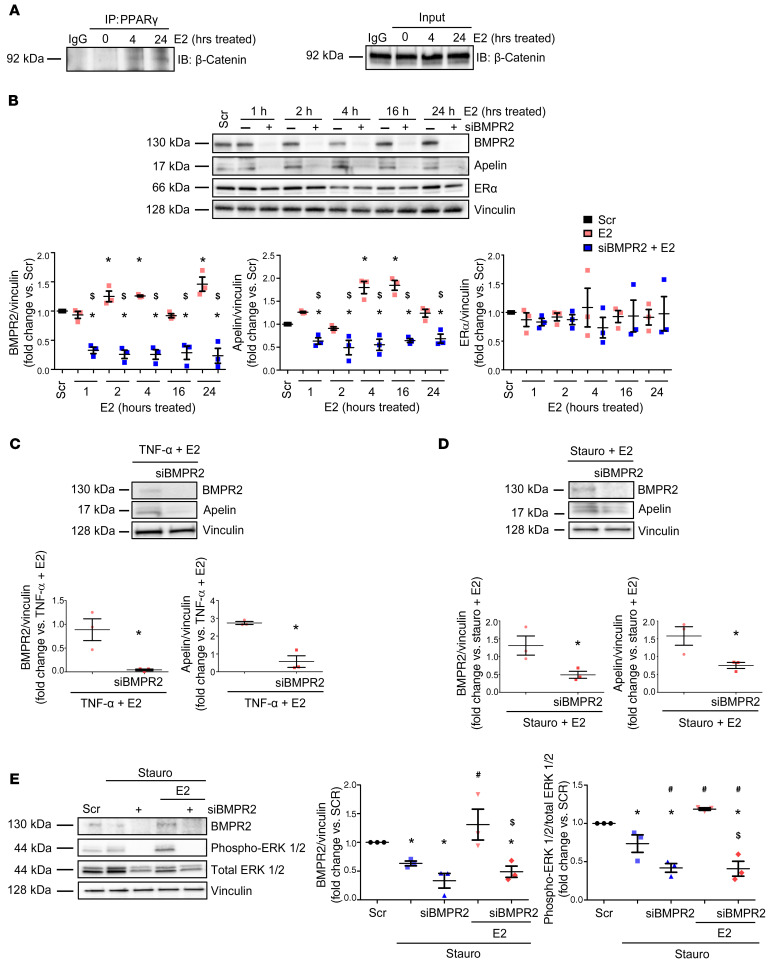
Figure 11. E2 induces formation of PPARγ/β-catenin complexes and requires BMPR2 to increase apelin expression or ERK1/2 activation in cardiomyoblasts.
(A) H9c2 cardiomyoblasts were treated with E2 (100 nM) for 0, 4, or 24 hours and then immunoprecipitated with PPARγ antibody or rabbit IgG isotype control. Input control for each sample is indicated (bottom). Note formation of PPARγ/β-catenin complexes with E2 treatment at 4 and 24 hours. (B) Time course of siRNA knockdown of BMPR2 (5 nM) effects on apelin protein expression in E2-treated (100 nM) H9c2 rat cardiomyoblasts at baseline conditions. (C and D) Effects of BMPR2 knockdown on E2-mediated upregulation of apelin in stressed cardiomyoblasts. H9c2 cells were pretreated with E2 (100 nM, 24 hours) and then stressed with TNF-α (10 ng/ml, 8 hours; C) or staurosporine (stauro; 50 nM, 4 hours; D) with or without siRNA knockdown of BMPR2 (5 nM, 24 hours prior to E2). (E) Effects of BMPR2 knockdown on E2-mediated ERK1/2 activation in stressed cardiomyoblasts. Cells were pretreated with E2 (100 nM, 24 hours) and then treated with stauro (50 nM, 4 hours) with or without siRNA directed against BMPR2 (5 nM; 24 hours prior to E2 and stauro). Representative blots for 3 independent experiments shown in A and B–E. Densitometries include data from all experiments. Scr = scramble siRNA. *P < 0.05 versus Scr control, $P < 0.05 versus E2 by ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s correction in B; *P < 0.05 versus TNF + E2 or Stauro + E2 by Student’s t test in C and D; *P < 0.05 versus Scr control, #P < 0.05 versus Stauro, $P < 0.05 versus E2-treated Stauro group by ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett’s correction in E. Error bars represent mean ± SEM; each data point represents 1 experiment or animal.