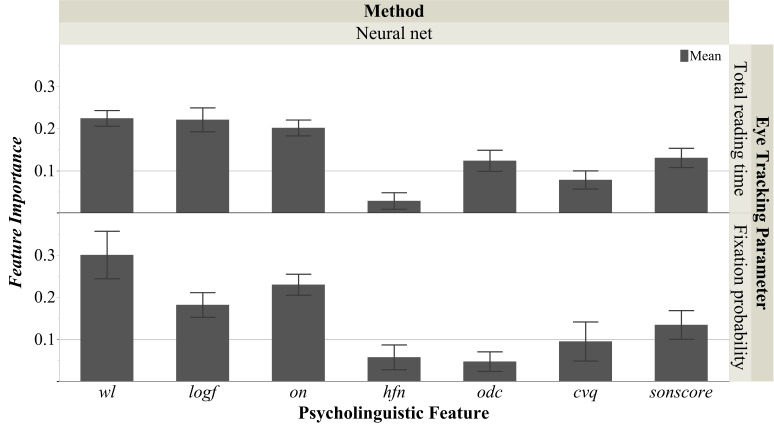
Figure 3.
Feature Importances for Total Reading Time and Fixation Probability. Figure 3 shows the feature importances (FIs) for the neural net model. The FIs were calculated by using the dependent resampled inputs option and mean total effects of 1000 iterations. The total effect is an index quantified by sensitivity analysis, which reflects the relative contribution of that feature both alone and in combination with other features (for details (79). All seven psycholinguistic features were computed for all unique words (word-type, 205 words, data for words appearing several times in the texts were the same) in the three sonnets based on the Gutenberg Literary English Corpus as reference (GLEC) (99): wl was the number of letters per word; logf was log transformed word, on was the number of words of the same length as the target differing by one letter, hfn was the number of orthographic neighbors with higher word frequency than the target word; odc was the target word’s mean Levenshtein distance from all other words in the corpus; cvq was the quotient of consonant and vowels in one word; sonscore was a simplified index based on the sonority hierarchy of English phonemes which yields 10 ranks (69, 34). Each error bar is constructed using 1 standard deviation from the mean. (Note that, because of the bad model fits (see Figure 2), the FIs in explaining first fixation duration were excluded from this figure).