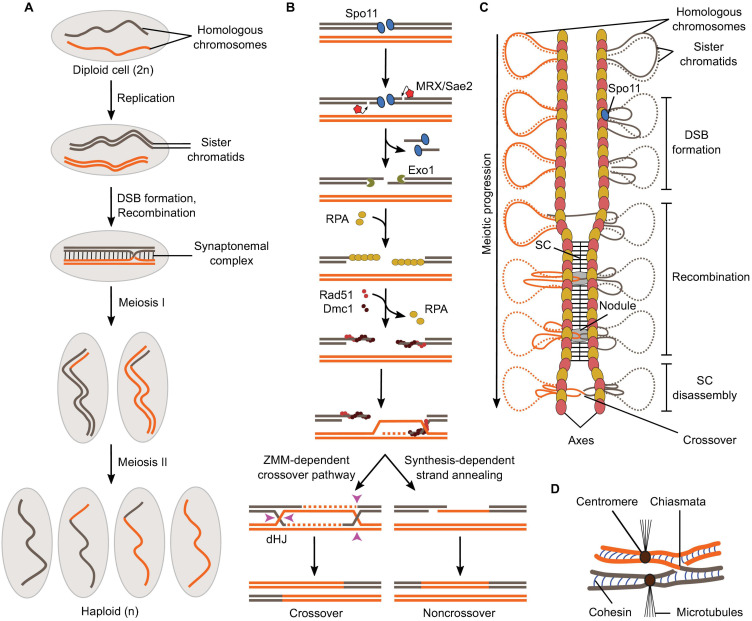
FIGURE 1.
Overview of meiosis and meiotic recombination. (A) Schematic of the formation of haploid gametes from a diploid cell with a single pair of homologous chromosomes. DSB formation and recombination promote homolog pairing and lead to the exchange of chromosomal fragments (crossovers) in the context of synapsed chromosomes. (B) Meiotic recombination is initiated by Spo11-mediated DSB formation and leads to the formation of crossovers via a ZMM-dependent double Holliday Junction (dHJ) resolution pathway or non-crossovers by synthesis-dependent strand annealing. (C) Relationships between meiotic recombination and higher-order chromosome structure. DSB formation happens in the context of the loop-axis structure. As recombination progresses, the SC polymerizes between the axes and is disassembled prior to chromosome segregation. Axis proteins Red1 (red ovals) and Hop1 (yellow ovals) are shown. (D) In metaphase I, homologs are held together through chiasmata and sister chromatid cohesion.