Fig. 3. Knockdown of microglial IL4Rα decreased the Arg1+ microglia phenotype in the hippocampus and increased the vulnerability of mice to stress.
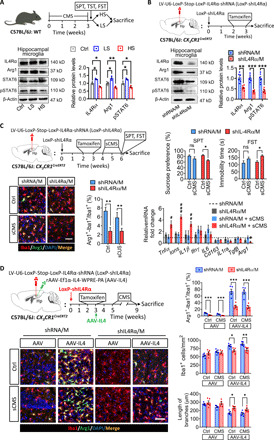
(A) Western blotting shows the levels of IL4Rα, Arg1, STAT6, and pSTAT6 in the hippocampal microglia of LS and HS mice (n = 3). (B) Western blotting shows the levels of IL4Rα, Arg1, STAT6, and pSTAT6 in the hippocampal microglia of LoxP-shIL4Rα–injected CX3CR1Cre/ERT2 mice after tamoxifen treatment (n = 6). (C) Effects of knockdown microglial IL4Rα combined with sCMS exposure on depressive-like behaviors, percentage of Arg1+ microglia, and cytokine expression of CX3CR1Cre/ERT2 mice (n = 8 for behavioral analysis, n = 6 for quantification of Arg1+ microglia, n = 4 to 6 for analysis of cytokine expression). Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Effects of microglial IL4Rα knockdown in the hippocampus on the ratio of Arg1+ microglia, number, and length of branches of Iba1+ cells (n = 5). Scale bar, 50 μm. Data are presented as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005, one-way ANOVA with Tukey test (A), two-tailed t test (B), two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni test for behavioral analysis (C), and two-way ANOVA with Tukey test for quantification of Arg1+ microglia (C), #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.005 versus shRNA/M + sCMS group, two-way ANOVA with Tukey test for analysis of cytokine expression (C).
