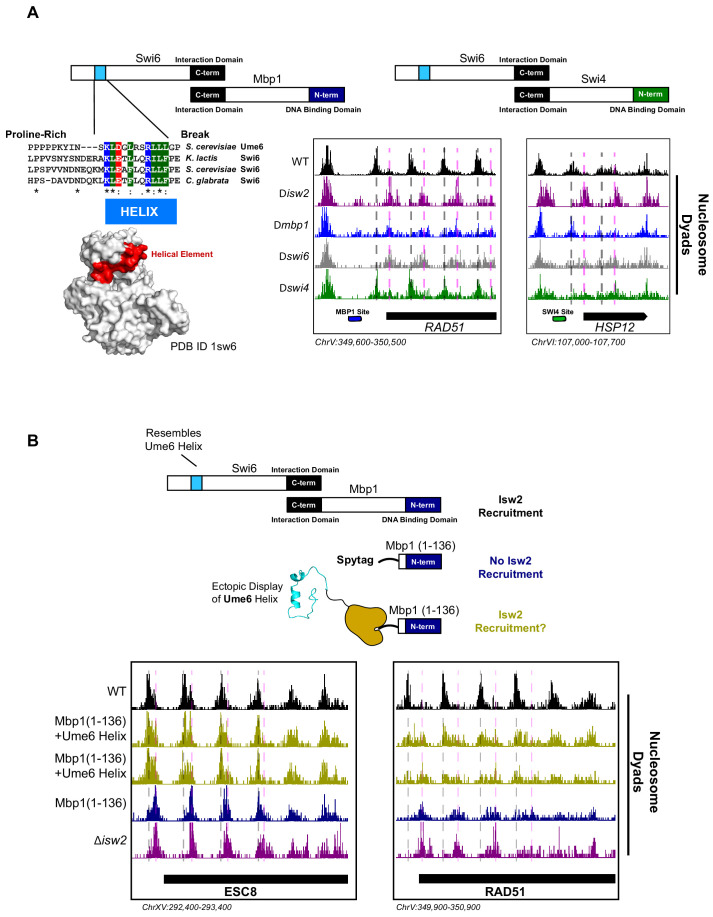
Figure 3. The cell cycle regulator Swi6 contains a similar helical element and recruits Isw2 to MBF and SBF target genes.
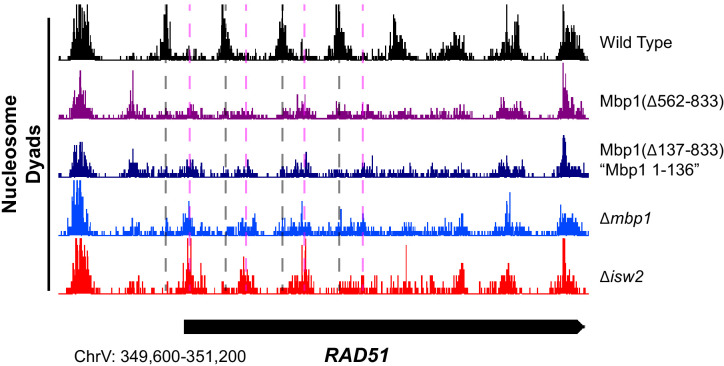
(A) (Top left) Schematic representation of the Swi6-Mbp1 MBF complex. Swi6 interacts with Mbp1 through the C-terminal domain (black rectangle). Mbp1 has an N-terminal DNA binding domain (dark blue rectangle). The putative Isw2-recruitment helix is in the Swi6 N-terminus (light blue rectangle). (Center left) Conserved residues in the putative Isw2-recruitment helix in Swi6 for three yeast species compared to the Isw2-recruitment helix in Ume6 for S. cerevisiae. (Bottom left) Crystal structure (Protein Data Bank [PDB] ID 1sw6) showing the location of the surface-exposed, conserved helical element from Swi6 in red. (Top right) Schematic representation of the Swi6-Swi4 SBF complex. Swi6 interacts with Swi4 through the C-terminal domain (black rectangle). Swi4 has an N-terminal DNA binding domain (green rectangle). Putative Isw2-recruitment helix is shown (small blue rectangle). (Bottom center) Genome Browser image showing nucleosome dyad signal for indicated strains at the RAD51 locus, an MBF target gene with an indicated Mbp1 binding motif (blue rectangle). Wild-type (WT) nucleosome positions are indicated by vertical dashed gray lines while ectopic positions associated with isw2, mbp1, and swi6 deletion strains are indicated by vertical dashed pink lines. (Bottom right) Genome Browser image showing nucleosome dyad signal for indicated strains at the HSP12 locus, an SBF target gene with an indicated Swi4 binding motif (green rectangle). WT positions are denoted by vertical gray dashed lines while ectopic nucleosome positions associated with isw2, swi6, and swi4 deletion strains are indicated with vertical pink dashed lines. (B) (Top) Schematic representation of constructs used to determine if ectopic display of an Isw2-recruitment helix on the Mbp1 N-terminus could recover Isw2-positioned nucleosomes at Mbp1 target genes. Either WT Mbp1, a C-terminal deletion of Mbp1 leaving only the DNA binding domain and an appended SpyTag, or a C-terminal deletion of Mbp1 leaving the DNA binding domain and SpyTag with constitutively expressed SpyCatcher fused to the Isw2-recruitment helix from Ume6 was examined. (Bottom) Genome Browser image showing nucleosome dyad signal for indicated strains at the ESC8 (left) or RAD51 (right) loci. Gray vertical dashed lines indicate WT nucleosome positions while vertical dashed pink lines indicate ectopic nucleosome positions associated with inactive Isw2 or Mbp1/Swi6. Biological replicates for ectopic display of the recruitment helix are provided as two separate tracks (gold) to emphasize reproducibility.