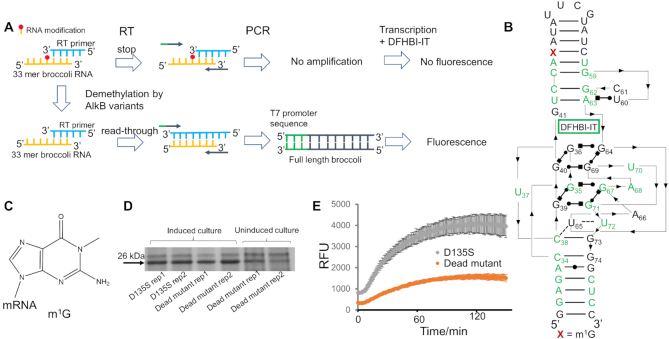
Figure 1.
Establishment of the high-throughput screening system for AlkB. (A) The scheme of the Broccoli RNA fluorescence assay for high-throughput screening of AlkB activity towards modifications in RNA. RT: reverse transcription. DFHBI-IT is the fluorophore that the Broccoli RNA binds to. (B) The 51 nt Broccoli RNA sequence with conservative bases labeled in green. Thin lines with arrows denote chain connectivity and the Leontis-Westhof symbols denote canonical and non-canonical base pairs (26). The structure is based on the secondary structure of Spinach 1.2 and the high similarity of their core domains (12,13). The numbering scheme for Broccoli follows Filonov et al. (11) and is used throughout. The 51 nt consists of nucleotides numbering from 29 to 79, and the 33 mer substrate used in our assay consists of nucleotides numbering from 29 to 61, with m1G located at site 46. (C) The chemical structure of m1G. (D) D135S and the catalytically dead mutant are expressed at the same level in E. coli cells. (E) Demethylation activity of D135S versus the catalytically dead mutant from E. coli crude lysates on m1G in the RNA. Error bar indicates SD, n≥3.