Figure 6.
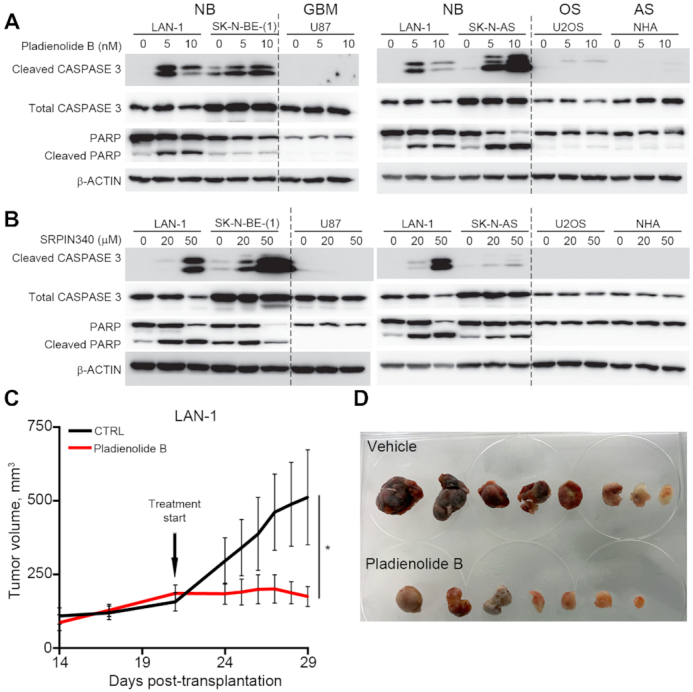
Pharmaceutical inhibition of spliceosome activity selectively induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells and impedes neuroblastoma xenograft growth. (A) Induction of apoptosis in LAN-1,SK-N-BE(1) and SK-N-AS neuroblastoma (NB) cells, but not in human glioma (GBM) cells (U87), osteosarcoma (OS) cells (U2OS) or normal human astrocytes (AS), (NHA) upon pladienolide B treatment (0–20 nM) for 48 h, as detected by western blotting of full-length CASPASE-3, cleaved CASPASE-3, full-length PARP and cleaved PARP; β-ACTIN was used as a loading control. (B) Induction of apoptosis in LAN-1,SK-N-BE(1) and SK-N-AS neuroblastoma cells (NB), but not in human glioma (GBM) cells (U87), osteosarcoma cells (U2OS) or normal human astrocytes (NHA) upon SRPIN340 treatment (0–50 mM) for 48 h, as detected by western blotting of full-length CASPASE-3, cleaved CASPASE-3, full-length PARP and cleaved PARP; β-ACTIN was used as a loading control. LAN-1 cells were included in all western blots (A, B) for comparison. (C, D) In mice xenografted with LAN-1 neuroblastoma cells, treatment with Pladienolide B significantly reduced tumor growth (n = 7–8) (C, D). *P<0.05; Mixed-effects model with Geisser-Greenhouse's epsilon correction.
