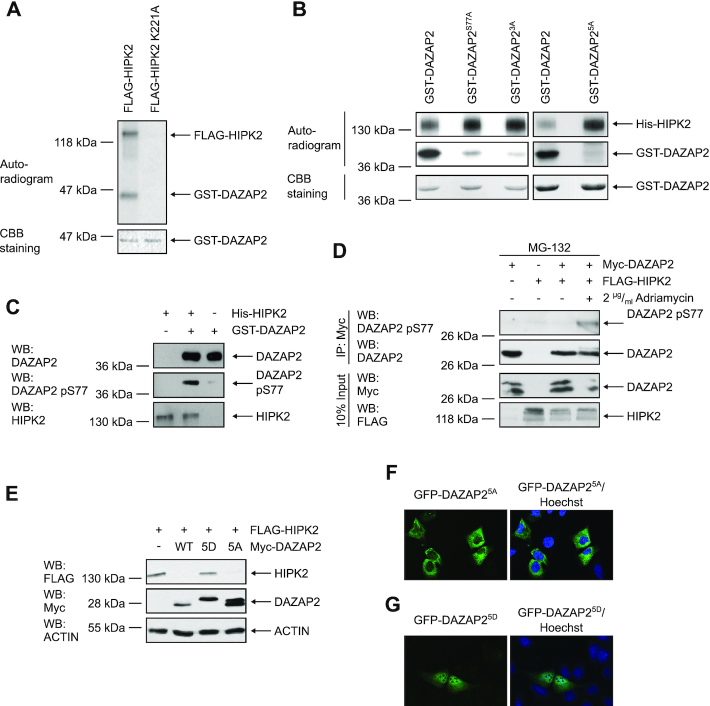
Figure 5.
Phosphorylation of DAZAP2 by HIPK2 regulates DAZAP2-mediated HIPK2 degradation and DAZAP2 localization. (A) FLAG-HIPK2 and kinase-dead FLAG-HIPK2 K221A were purified from 293T cells, recombinant GST-DAZAP2 was purified from E. coli. In vitro kinase assays were performed and DAZAP2 phosphorylation as well as HIPK2 autophosphorylation were examined by autoradiography. Protein levels were analyzed by Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining. n = 2. (B) HIPK2 phosphorylates DAZAP2 on five Ser/Thr residues. In vitro kinase assays were performed using bacterially expressed His-HIPK2 and GST-DAZAP2 mutants and analyzed by SDS–PAGE and autoradiography. Protein levels were analyzed by CBB staining. n = 3. (C) Validation of the DAZAP2 phospho-Ser77 antibody. In vitro kinase assays were performed with His-HIPK2 and GST-DAZAP2. Non-phosphorylated GST-DAZAP2 and in vitro phosphorylated GST-DAZAP2 phosphorylation were examined by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting. n = 3. (D) DAZAP2 is phosphorylated at Ser77 upon DNA damage in cells. Proteins were expressed in H1299 cells as indicated in the presence of the indicated compounds. Myc-DAZAP2 was precipitated from the lysates and analyzed by immunoblotting as indicated. n = 2. (E) Effect of DAZAP2 phosphorylation on its HIPK2-degrading capacity. H1299 cells were transfected with the indicated expression vectors and total protein lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. n = 3. (F, G) DAZAP2 phosphorylation regulates its localization. The indicated EGFP-DAZAP2 fusion proteins were expressed in U2OS cells and their subcellular localization was assessed by confocal microscopy. DNA is stained by Hoechst (blue). n = 3. DAZAP23A: S77A, S85A, T86A; DAZAP25A: S62A, S69A, S77A, S85A, T86A; DAZAP25D: S62D, S69D, S77D, S85D, T86D. Representative experiments are shown.