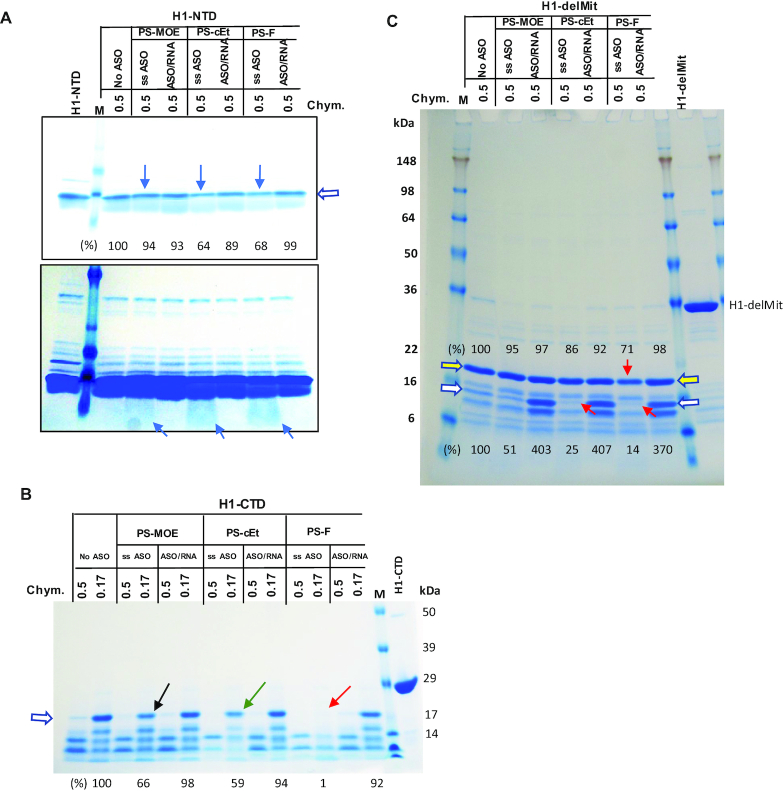
Figure 4.
Limited proteinase digestion of RNase H1 domains. (A) Purified H1-NTD protein was incubated with ss-PS-ASOs of different 2′-modifications or with PS-ASO/RNA duplexes (Figure 1C, right panel), and subjected to digestion with 2.5 μl 0.5 mg/ml of chymotrypsin (Chym), as described in Materials and Methods. The digested proteins were separated on 10–12% SDS-PAGE in MOPs buffer (A, B), followed by coomassie blue staining. The arrows indicate increased digestion upon binding to ss-PS-ASOs. The signal intensity of the top band (marked by open arrow) was quantified and shown below the lanes. Lower panel, a stronger signal intensity. (B) Coomassie blue staining of H1-CTD protein incubated with PS-ASOs or ASO/RNA duplexes, as in panel A, followed by digestion with different concentrations of chymotrypsin. The arrows indicate enhanced digestion by ss-PS-ASOs compared with no ASO. The bands denoted by the open arrow were quantified using ImageJ and normalized to that in no ASO control sample, which were digested by the 0.17 mg/ml chymotrypsin. (C) Purified H1-delMit protein was incubated with ss-PS-ASOs of different 2′ modifications or with PS-ASO/RNA duplexes, and subjected to digestion with 0.5 mg/ml of chymotrypsin (Chym). The digested proteins were separated on 10–12% SDS-PAGE in Tris-glycine buffer, followed by coomassie blue staining. The red arrows indicate increased digestion upon binding to ss-PS-ASOs. The protected fragments by the duplex are marked with an open white arrow. The protein bands denoted by open arrows were quantified using ImageJ and normalized to that in no ASO control sample. The relative levels of the peptides are listed on the top for the band marked with a yellow arrow; at the bottom for the band marked with a white arrow.