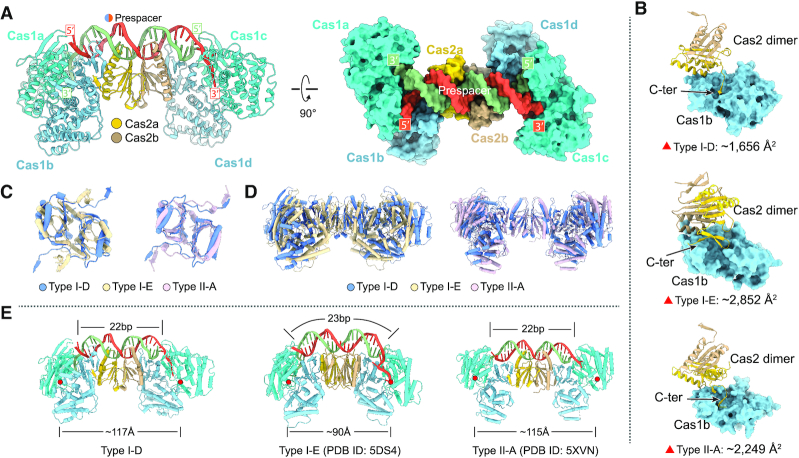
Figure 2.
Crystal structure of Synechocystis type I-D Cas1–Cas2–prespacer complex and structural comparison. (A) Ribbon diagram of Synechocystis type I-D Cas1–Cas2–prespacer complex structure. The Cas1a and Cas1c are colored in cyan, Cas1b and Cas1d are colored in light blue, and the two monomers of Cas2 are colored in yellow and brown, respectively. The prespacer DNA is colored in red and blue. (B) The interaction details of Cas1 and Cas2 in various types (type I-D: Synechocystis, type I-E: E. coli, type II-A: E. faecalis). The buried areas of interaction interfaces are indicated. (C) Comparison of Cas2 dimer of various types. One protomer of the Cas2 dimer was aligned, the other displayed obvious rotation as indicated. (D) Comparison of Cas1–Cas2 complex of various types with overlayed Cas2 dimer. (E) Comparison of the DNA binding architecture of Cas1–Cas2 complex from various types. The length of prespacer duplex and the distance between the active sites of the two catalytic Cas1 unites are labeled. The Cas1 active sites are indicated by red circles.