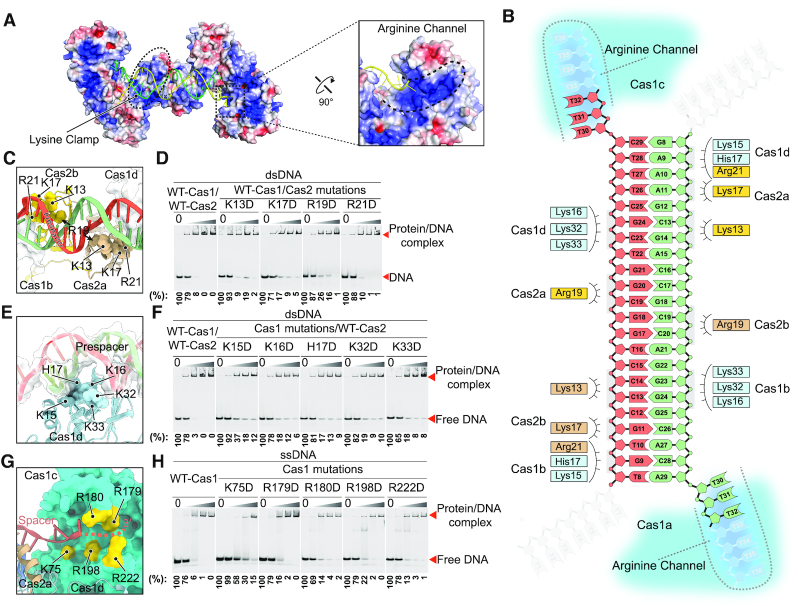
Figure 3.
Coordination of the prespacer by the Cas1–Cas2 complex. (A) Electrostatic potential surface representation of the Cas1–Cas2 complex with the prespacer colored in green and yellow. Blue and red (±5 kT/e) indicate the positively and negatively charged areas, respectively, of the protein complex. The lysine clamp and arginine channel responsible for coordinating the prespacer are highlighted in dashed line. (B) Diagram of the prespacer and residues coordinating the prespacer. (C) Details of the prespacer coordinated by residues of Cas2 lysine clamp. Coloring is as in (b). (D) EMSA assay for assessing the effect of charge reversal mutation of Cas2 residues involved in prespacer coordination. The protein and DNA concentrations are same as in Figure 1F. Percent of the free DNA is calculated based on the gray scanning analysis. (E) Close up view of the prespacer coordination by Cas1 lysine clamp residues. Coloring is as in (B). (F) Charge reversal mutation of Cas1 lysine clamp residues weakens binding affinity between Cas1–Cas2 complex and the prespacer as shown by EMSA. The protein and DNA concentrations are same as in Figure 1F. (G) Detailed view of the arginine channel that stabilizes the 3′ overhang of the prespacer. (H) Mutation of key arginine channel residues impairs the ssDNA binding ability of Cas1.