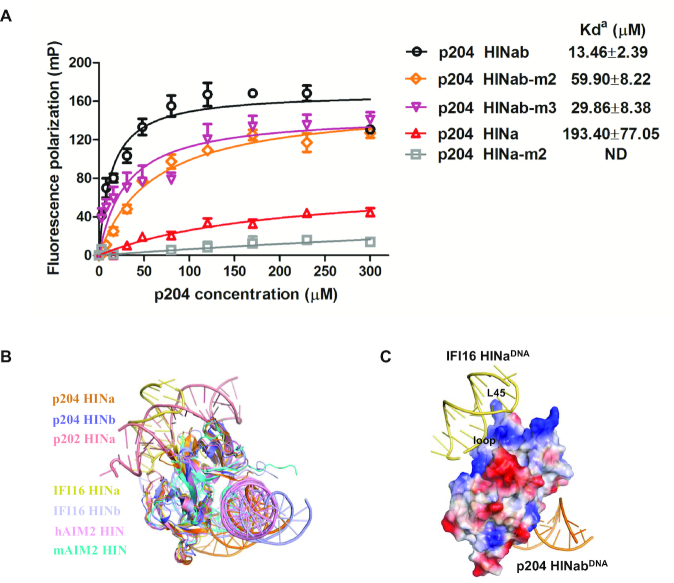
Figure 5.
The DNA-binding mode of HIN domains in PYHIN family. (A) FP assays of the DNA-binding interface of p204 HINab and HINa binding to 30 mer dsDNA. The apparent Kd values (Kda) are shown for p204 HINab, HINa and mutants. ND means not determined. (B) Structural comparison of HIN domains in complex with DNA. Structures of p204 HINa:DNA (orange) and HINb: DNA (slate) are from HINab:dsDNA complex. Structures of p202 HINa (PDB: 4L5R), human AIM2 HIN (PDB: 3RN2), murine AIM2 HIN (PDB: 4JBM), IFI16 HINa (PDB: 4QGU) and IFI16 HINb (PDB: 3RNU) are shown in salmon, pink, cyan, yellow orange and light blue, respectively. (C) Positive surface electrostatics of p204 HINa facing the DNA from the complexc of IFI16 HINa:DNA. It was set to 20% transparency. The loop between α3 and IIβ1, and L45 of OB2 on p204 HINa are labeled.