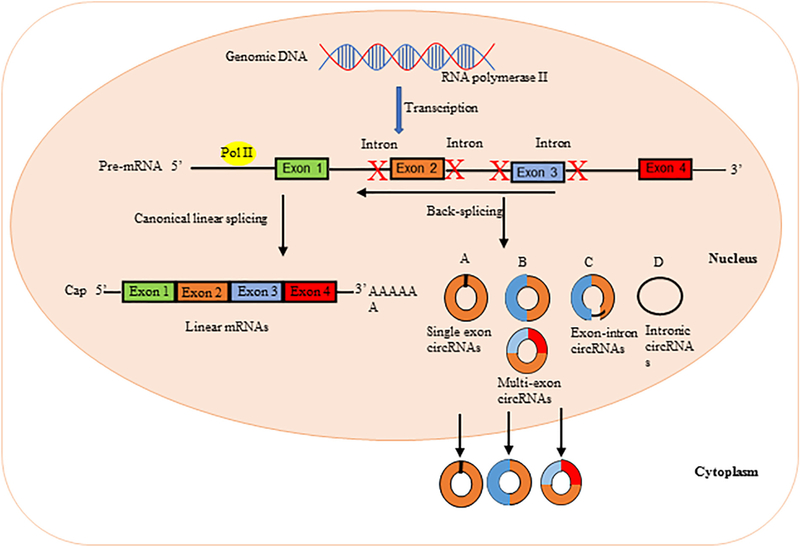
Fig. 2A.
Schematic representation illustrating circRNA biogenesis. In the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, DNA is transcribed to form precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA), which contain coding exons and introns. Different from linear mRNAs, which are formed by canonical linear splicing and cutting away introns of the pre-mRNAs using small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs), circular RNAs (circRNAs) are formed by back-splicing of the pre-mRNAs and circularization of the cut segment, where the 5’ end joins the 3’ end. (A) Single exon circRNAs: circular RNAs can be generated from a single exon; (B) Multi-exon circRNAs: circular RNAs can also be generated from two or more exons; (C) Exon-intron circRNAs: circular RNAs can contain intron(s) that have been retained between one or more circular exons; (D) Intronic circRNAs: introns can be excised from pre-mRNAs and circularize to give rise to circRNAs.