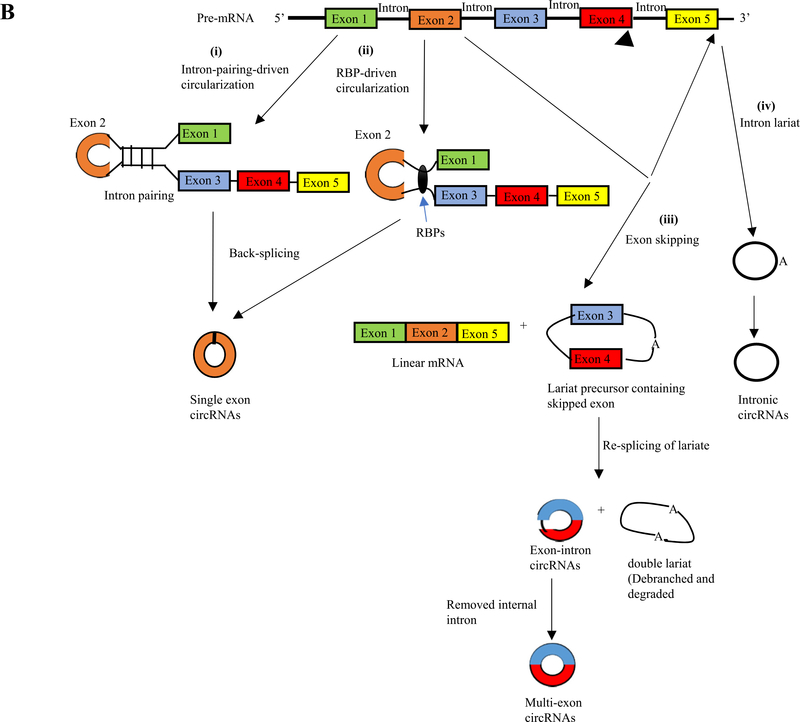
Fig. 2B.
The proposed models of circRNA formation. i) Intron-pairing-driven circularization. Two complementary introns form a circular structure containing several introns and exons through a base-pairing connection. Finally, introns are removed to form exonic circRNAs (EcircRNAs). ii) RNA binding protein (RBP)-driven circularization. The binding of RBPs acts as a vehicle that binds two non-adjacent introns. Then circRNAs are generated after the removal of introns. iii) Exon skipping: the back-splicing process can take place because of exon skipping mechanism, which leads to lariat formation. This process can generate three different products: linear mRNA, an exonic or exonic-interonic circRNAs, and intron lariats iv) Intron lariat will generate intronic circRNAs.