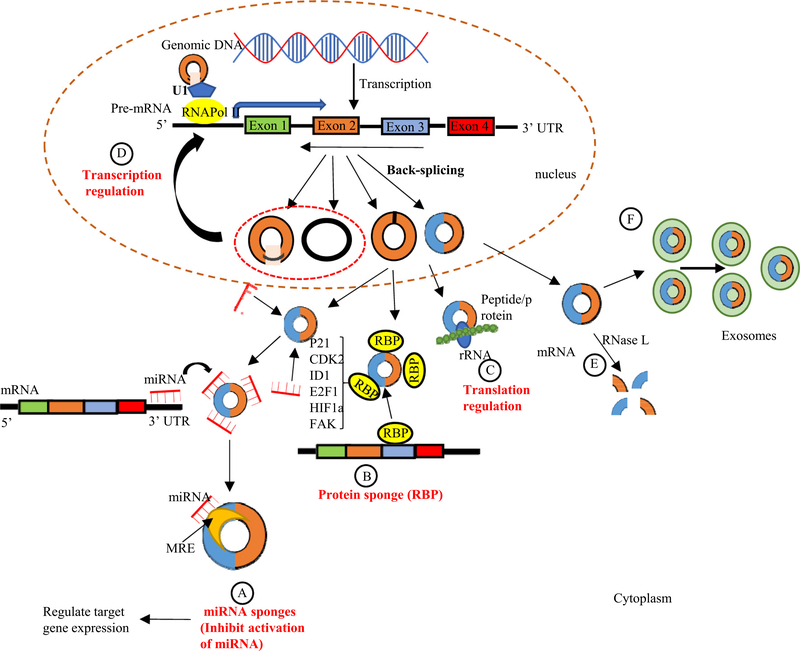
Fig. 4.
Schematic representation of circRNA functions and degradation. (A)microRNA sponges: circRNAs can act as miRNA sponges by competing for miRNA binding sites (miRNA response elements (MREs)) and prevents miRNA from interacting with their target messenger RNA (mRNA) at 3’ untranslated region (UTR) leading to reduced the effect of miRNA-mediated regulatory activities.(B) Interaction with RNA binding proteins (RBPs): circRNAs may act as protein sponges, by directly binding to RBPs, and therefore retain them in the cytoplasm. These RBPs includes: cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (p21), cyclin-dependent protein kinase 2 (CKD2), inhibitor of DNA binding 1 (ID1), E2F1, Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF1a), and preface focal adhesion kinase (FAK). (C) CircRNA can be translated with ribosome and encode peptides or proteins. (D) CircRNAs (e.g. EIciRNAs and ciRNAs) may interact with transcription complexes and enhance the expression of their parental genes. (E) The degradation of circRNAs. CircRNAs are globally degraded by RNase L in early cellular innate immune responses. (F) The elimination of circRNAs. circRNAs can be eliminated into the extracellular space by exosomes