Figure 3.
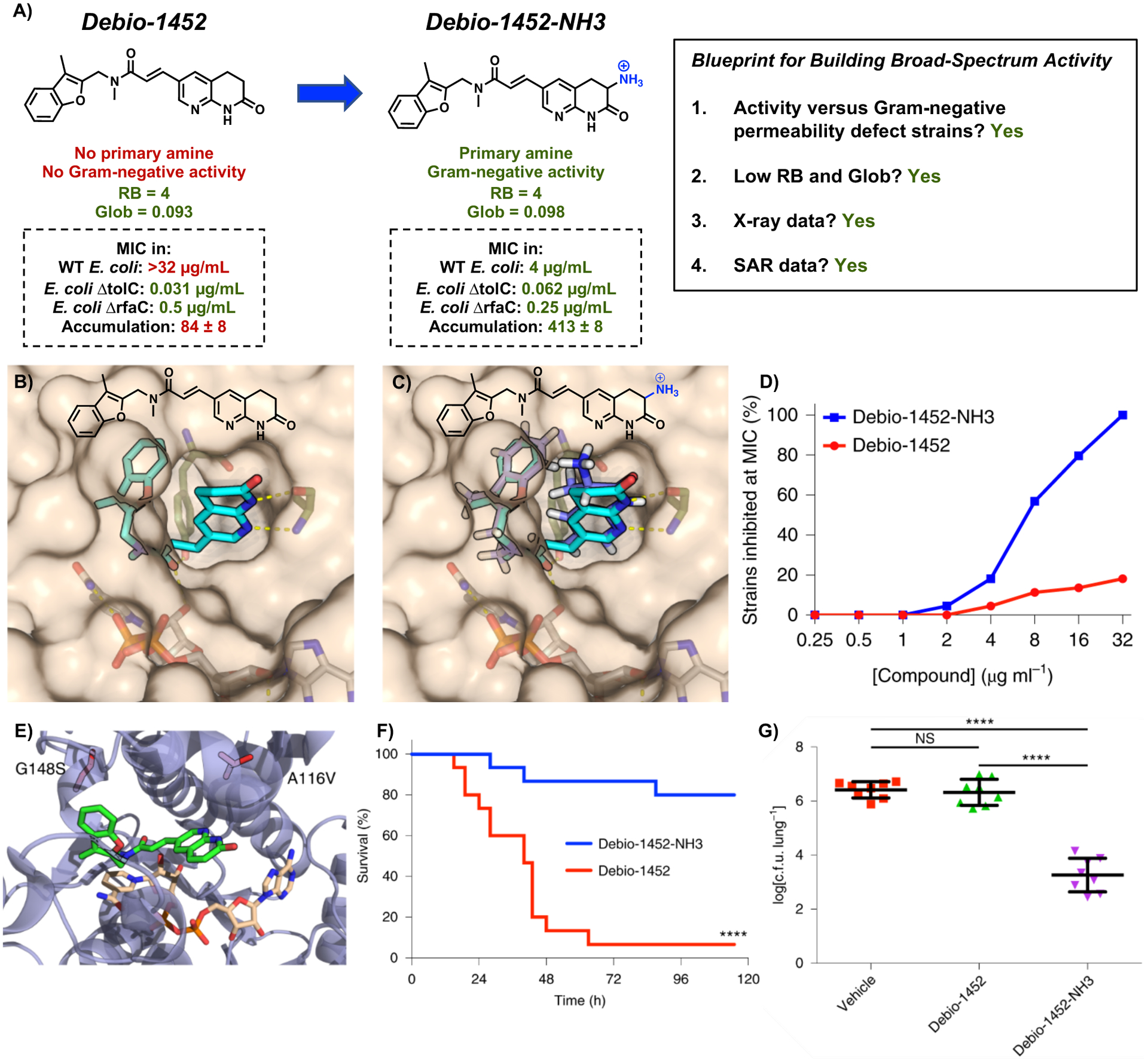
(A) Conversion of Debio-1452 into Debio-1452-NH3. WT E. coli is strain MG1655. Accumulation is reported in nmol per 1012 colony-forming units (CFUs). The s.e.m. is reported for accumulation values. (B) Solvent exposure of the naphthyridinone ring of Debio-1452 when bound to S. aureus FabI suggests sites for modification. (C) Computational docking of Debio-1452-NH3 overlaid with the crystal structure of Debio-1452. (D) Evaluation of Debio-1452 and Debio-1452-NH3 against a panel of 44 Enterobacteriaceae clinical isolates. All experiments were performed in biological triplicate. (E) Locations of E. coli FabI amino acid substitutions conferring resistance to Debio-1452-NH3. (F) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of mouse efficacy model of sepsis induced with A. baumannii W41979. Statistical significance was determined by two-tailed log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. (G) Bacterial burden model of acute pneumonia in mice infected with K. pneumoniae BAA-1705. Data are shown as means ± s.d. and statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons. NS, not significant (P > 0.05); ****P < 0.0001. Reproduced with permission from ref. 2. Copyright 2020 Nature Microbiology.
