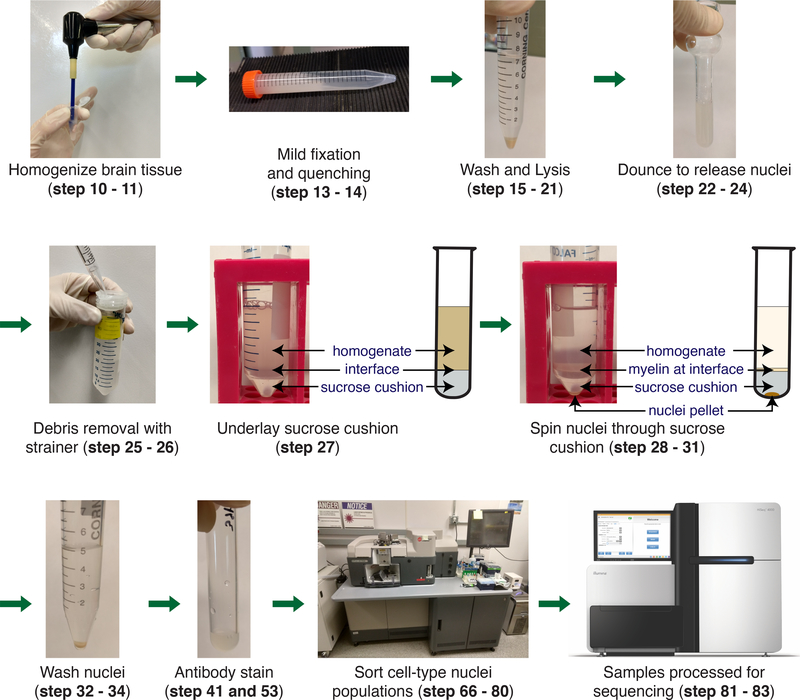
Fig. 1 |. Schematic of cell type-specific nuclei isolation from frozen brain tissue.
The brain is homogenized in 1% (wt/vol) formaldehyde in DPBS (steps 10 – 11). The homogenate is fixed for 10 mins followed by a 5 min quenching (steps 13 – 14). Homogenate is washed and then lysed in NF1 buffer on ice for 30 min (steps 15 – 21). Nuclei are released by douncing (steps 22 – 24). To remove large debris the homogenate is passed through a 70 μm strainer (steps 25 – 26). To remove the myelin a sucrose cushion is first underlayed (steps 27). The nuclei are then pelleted by centrifugation and the myelin remains at the interphase (steps 28 – 31). The nuclei pellet is washed with NF1 buffer and FACS buffer (steps 32 – 34). The nuclei are stained for cell type-specific markers (steps 41 and 53). Nuclei populations are isolated by sorting on a FACS machine (steps 66 – 80). Nuclei are processed for downstream sequencing applications (steps 81 – 83).