Figure 10: L. plantarum reverses ethanol-induced neuroinflammation.
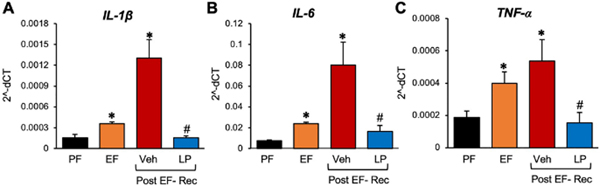
Adult female mice were fed a liquid diet with ethanol (EF) or isocaloric maltodextrin (PF) for 4 weeks, following which ethanol was withdrawn for 24 hours by feeding the liquid diet without ethanol, but with (LP) or without (Veh) L. plantarum. The mRNA levels for IL-1β (A), IL-6 (B), and TNF-α (C) in the plasma were measured before and at 24 hours after ethanol withdrawal (Post EF-Rec) were measured in the cerebral cortex. Values are means ± sem (n = 6). Asterisks indicate the “EF” (pre and post ethanol withdrawal) values that are significantly (p-value < 0.05) different from corresponding “PF” values. The hashtags indicate the “Post EF-Rec + LP” values different from corresponding “Post EF-Rec + Veh” values.
