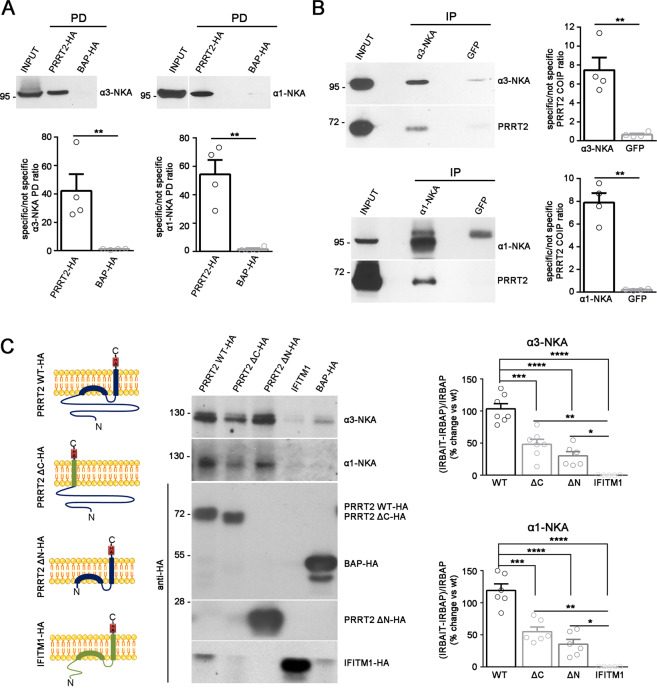
Fig. 1. PRRT2 interacts with α3-NKA and α1-NKA subunits.
A Pulldown of α3-NKA and α1-NKA by PRRT2: Affinity-purified PRRT2-HA or BAP-HA were incubated with total mouse brain extracts. After pulldown (PD), pellets were solubilized and subjected to western blotting with α3-NKA and α1-NKA antibodies. Mouse brain lysates incubated with PRRT2-HA showed specific immunoreactivity for α3-NKA and α1-NKA in the precipitates, which were not detected with BAP-HA. Top: Representative immunoblots are shown. Bottom: Quantification of the α3-NKA and α1-NKA immunoreactivities in the pulled down samples normalized to the BAP-HA control (means ± SEM, n = 4 independent experiments, **p < 0.01; unpaired Student’s t-test). Input, 10 μg total extract. B Co-immunoprecipitation of PRRT2 with α3-NKA and α1-NKA antibodies: Detergent extracts of mouse brain were immunoprecipitated (IP) with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to α3-NKA, α1-NKA or GFP (used as a control), as indicated. After the electrophoretic separation of the immunocomplexes and western blotting, membranes were probed with α3-NKA or α1-NKA antibodies to test the immunoprecipitation efficiency, as well as with polyclonal PRRT2 antibodies to test for co-immunoprecipitation. Left: Representative immunoblots are shown. Right: Quantification of the PRRT2 immunoreactive signal in the immunoprecipitated samples normalized to the GFP nonspecific signal (means ± SEM, n = 4 independent experiments, **p < 0.01; unpaired Student’s t-test). Input, 10 μg total extract. C Both the cytosolic and membrane-associated domains of PRRT2 are necessary for the interaction with NKA. Left: Schematics of the PRRT2 domain constructs. PRRT2ΔC-HA is a chimeric protein composed of the cytoplasmic domain of PRRT2 (violet) anchored to the membrane by the transmembrane domain of IFITM1 (green). PRRT2ΔN-HA is composed of the transmembrane domain of PRRT2. The IFITM1 protein (green) was used as a control. Middle: COS-7 cells were co-transfected with full length PRRT2 WT-HA, PRRT2ΔC-HA, PRRT2ΔN-HA, IFITM1-HA or BAP-HA constructs and either α3-NKA-SEP or α1-NKA-SEP constructs. Samples were immunoprecipitated by anti-HA beads (IP) and analyzed by western blotting with antibodies to α3-NKA, α1-NKA and HA. Representative immunoblots are shown. Horizontal white lines in the blot indicate that proteins of different molecular mass were separated on the same original gel and subjected to immunoblotting assays in distinct nitrocellulose strips. Right: Densitometric analysis of the fluorograms obtained in the linear range of the emulsion response. The immunoreactivity (IR) of the bait-specific pulldown with respect to the non-specific BAP control [(IRBAIT–IRBAP)/IRBAP] was calculated, normalized by the amount of each BAIT, and expressed in percent of the PRRT2 WT-HA. Means ± SEM of n = 6 independent experiments; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA/Tukey’s tests.