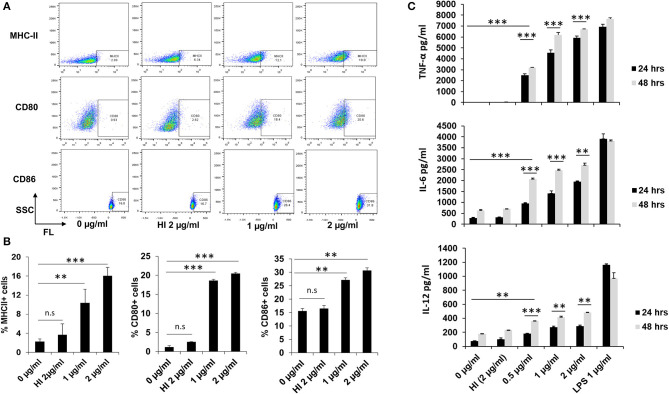
Figure 1.
RipA enhances the expression of macrophage activation markers and induces pro-inflammatory cytokines secretion. (A) The enhanced expression of surface markers of RAW264.7 cells (MHC-II, CD80, and CD86) at 24 h after treatment with medium alone, 1 μg/ml RipA, 2 μg/ml RipA, and HI RipA. The expression level was determined by FACS analysis using A488, PE, and APC-linked monoclonal antibodies, respectively. Purified RipA was treated with polymyxin B agarose for the removal of endotoxin, and 1 aliquot was digested with proteinase K, followed by heat inactivation at 100°C for 4 h. (B) Quantitative representation of the expression of MHC-II, CD80, and CD86 on the surface of RAW264.7 cells. (C) RAW264.7 cells were treated with RipA (0.5, 1, and 2 μg/ml), LPS 1 μg/ml, and HI RipA (2 μg/ml). After 24 and 48 h of treatment, cell culture supernatants were collected, followed by quantification of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-12 levels by sandwich ELISA. LPS was used as a positive control for the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Untreated and HI treated cells were used as negative controls. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments (3 replicates per experiment) and expressed as means ± SD. **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 vs. controls.