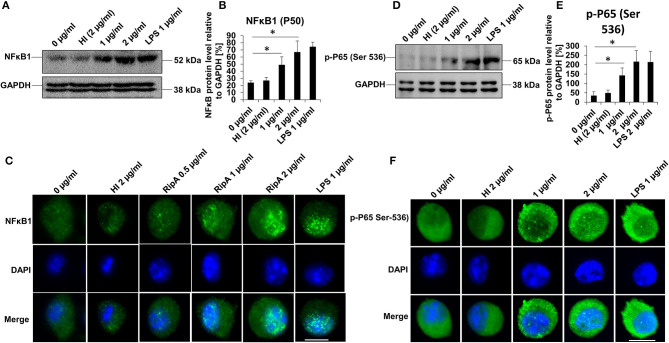
Figure 2.
RipA activates the canonical NFκB signaling pathway. (A) Western blots showing the expression level of NFκB1 (P-50) subunit in RipA-treated RAW264.7 cells. RAW264.7 cells were treated with RipA (1 and 2 μg/ml) for 24 h. The size and positions of the bands are marked on the figure. (B) Densitometric analysis of the P-50 subunit of NFκB. P-50 protein level was expressed relative to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) [%]. (C) Immunofluorescence microscopic images depicting nuclear translocation of P-50. Concentrations of RipA and antibody used are marked on the figure. (D) Western blots showing the level of the phosphorylated pP-65 subunit of NFκB in RipA treated RAW264.7 cells. (E) Densitometric analysis of pP-65 subunit. The pP-65 level was expressed relative to GAPDH [%]. (F) Immunofluorescence microscopic images showing nuclear translocation of phosphorylated P-65. DAPI was used to stain the nucleus. Untreated and HI treated cells were used as negative controls. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) treatment was used as a positive control. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments and quantification plot expressed as means ± SD. *p < 0.05 vs control. A488 conjugated secondary antibody was used for signal generation. Scale bar indicates 10 μm.